New Chaos RAT Variant Targets Windows and Linux in Recent Cyber Attacks
Cybersecurity analysts have identified a new variant of the Chaos remote access trojan (RAT) being used in attacks on both Windows and Linux systems.
According to Acronis researchers Santiago Pontiroli, Gabor Molnar, and Kirill Antonenko, this version of Chaos RAT appears to be distributed by deceiving users into downloading a fake network troubleshooting tool designed for Linux environments.
Chaos RAT is an open-source malware written in Golang and supports multiple platforms. It offers an administrative panel that allows users to create payloads, manage remote sessions, and control compromised devices. The tool is inspired by well-known frameworks such as Cobalt Strike and Sliver.
Although development of this RAT began as early as 2017, it did not attract much attention until December 2022, when it was used in attacks against public-facing Linux web applications. These attacks often involved deploying the XMRig cryptocurrency miner. Once installed, Chaos RAT connects to a remote server and awaits instructions. It can launch reverse shells, transfer and delete files, browse directories, capture screenshots, gather system data, perform machine reboots or shutdowns, and open URLs.
The most recent release of Chaos RAT is version 5.0.3, which became available on May 31, 2024.
Acronis reported that Linux versions of the malware have been spotted in active campaigns, especially those involving cryptocurrency mining. The typical infection method involves phishing emails that carry malicious links or attachments. These initiate the download of a harmful script that modifies the "/etc/crontab" task scheduler to repeatedly retrieve the malware, ensuring persistence on the system.
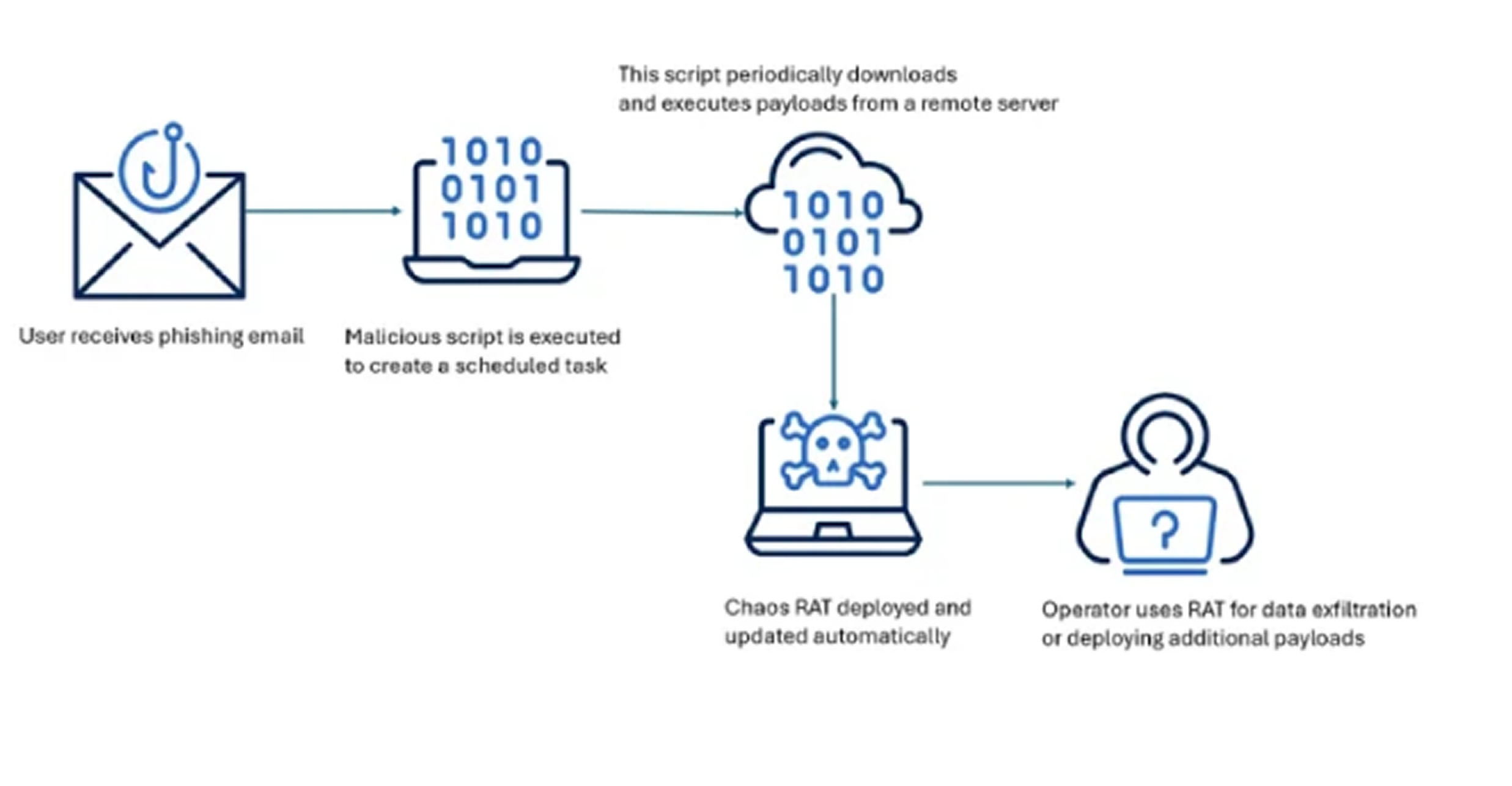
Earlier campaigns delivered Chaos RAT and cryptocurrency miners separately, suggesting that the RAT was originally used for reconnaissance and data collection on infected systems.
In January 2025, a malware sample named “NetworkAnalyzer.tar.gz” was uploaded to VirusTotal from India. This finding supports the theory that attackers are disguising the RAT as a legitimate Linux network diagnostic tool.
Security researchers also discovered vulnerabilities in the Chaos RAT admin panel. These include a command injection flaw (CVE-2024-30850, CVSS 8.8) and a cross-site scripting issue (CVE-2024-31839, CVSS 4.8). If exploited together, these vulnerabilities could allow attackers to execute commands on the server with elevated privileges. Both flaws were patched by the project maintainer in May 2024.
Although the individuals behind the current campaigns have not yet been identified, this case highlights how cybercriminals continue to exploit open-source tools to carry out sophisticated attacks while making attribution more difficult.
“What begins as a developer’s utility can quickly be turned into a weapon for threat actors,” the researchers explained. “Open-source malware provides an accessible and customizable toolkit. When widely adopted by multiple actors, it creates confusion around who is responsible for the attack.”
This discovery comes at the same time as another malicious campaign targeting Trust Wallet desktop users. Attackers are distributing fake wallet applications through phishing emails, malicious download links, and bundled software. The malware used in these attacks is designed to steal browser credentials, extract wallet data from both desktop software and browser extensions, execute remote commands, and act as clipper malware.
“Once installed, the malware scans for wallet files, monitors browser sessions, and captures clipboard data to steal seed phrases and private keys,” said Kedar S. Pandit, a researcher at Point Wild, in a new report.
Found this article interesting? Follow us on X(Twitter) ,Threads and FaceBook to read more exclusive content we post.