Google has revealed that the China-linked threat actor APT41 used a malware called TOUGHPROGRESS, which leverages Google Calendar as a command-and-control (C2)
channel, to target multiple government entities through a compromised government website. In late October 2024, Google’s Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) discovered the exploited website hosting the malware that was used to attack other government organizations. The report explains that abusing cloud services like Google Calendar for C2 helps threat actors blend their malicious traffic with legitimate activity, making detection more difficult.
APT41 delivered the malware via spear phishing emails containing a ZIP file hosted on the hacked government site. The ZIP file was disguised as a document about export declarations and included a malicious LNK file along with images of arthropods. Two of these images were fake, one contained an encrypted payload while the other held a DLL used to decrypt and launch the malicious code when the victim opened the file. A decoy PDF document was shown to the victim to avoid suspicion.
The malware executes in three stealthy stages with advanced evasion techniques. The first stage, called PLUSDROP, decrypts and runs the second stage entirely in memory. The second stage, PLUSINJECT, uses process hollowing to inject malicious code into legitimate Windows processes such as svchost.exe. The final stage, TOUGHPROGRESS, performs the attacker’s tasks and communicates with operators through Google Calendar to evade detection.
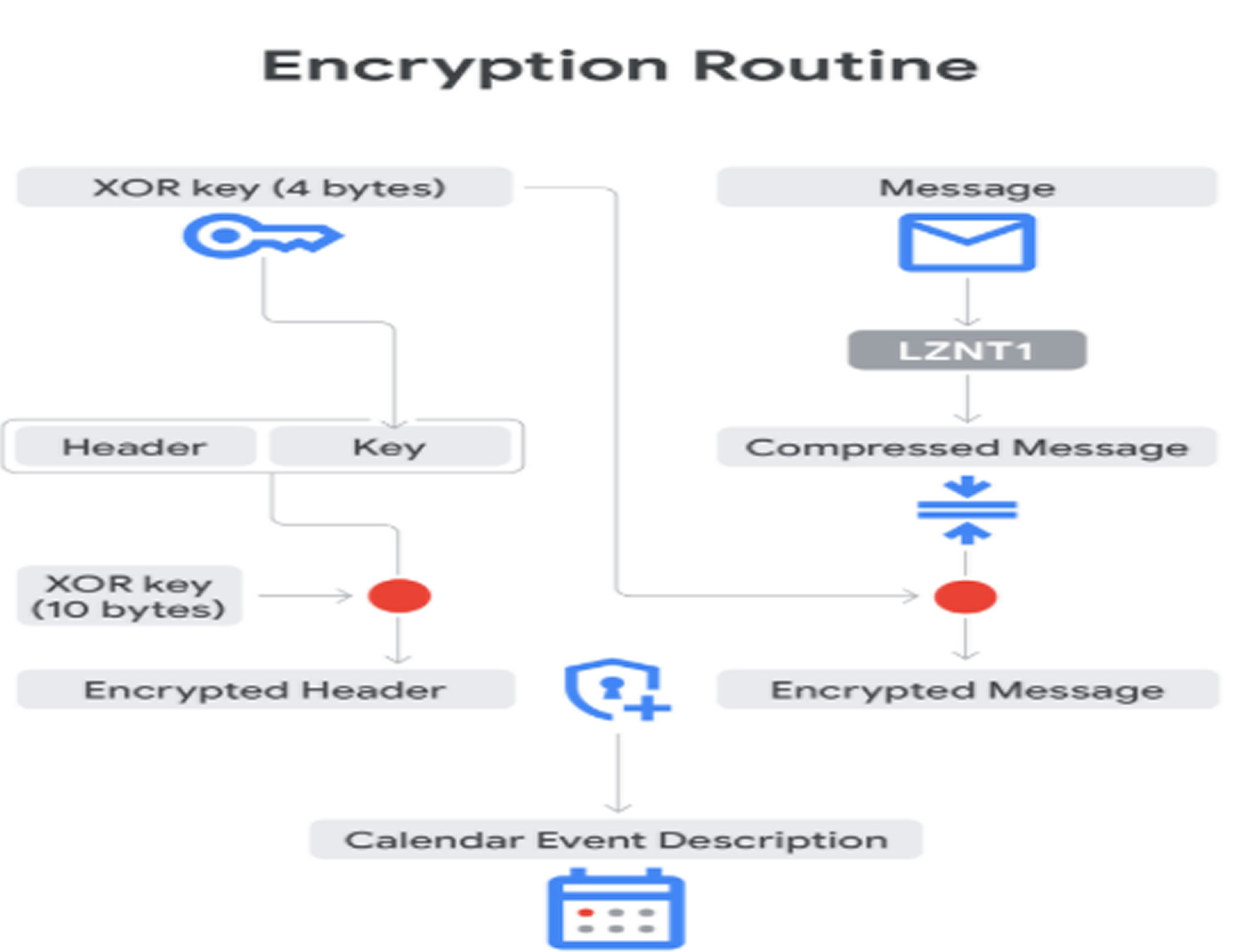
TOUGHPROGRESS begins by decrypting embedded shellcode with a hardcoded XOR key and decompressing a DLL in memory using LZNT1 compression. The DLL employs complex control flow obfuscation techniques including register-based indirect calls, dynamic address arithmetic, 64-bit register overflow, and function dispatch tables, making it difficult for security tools and analysts to understand its behavior or reverse engineer the malware.
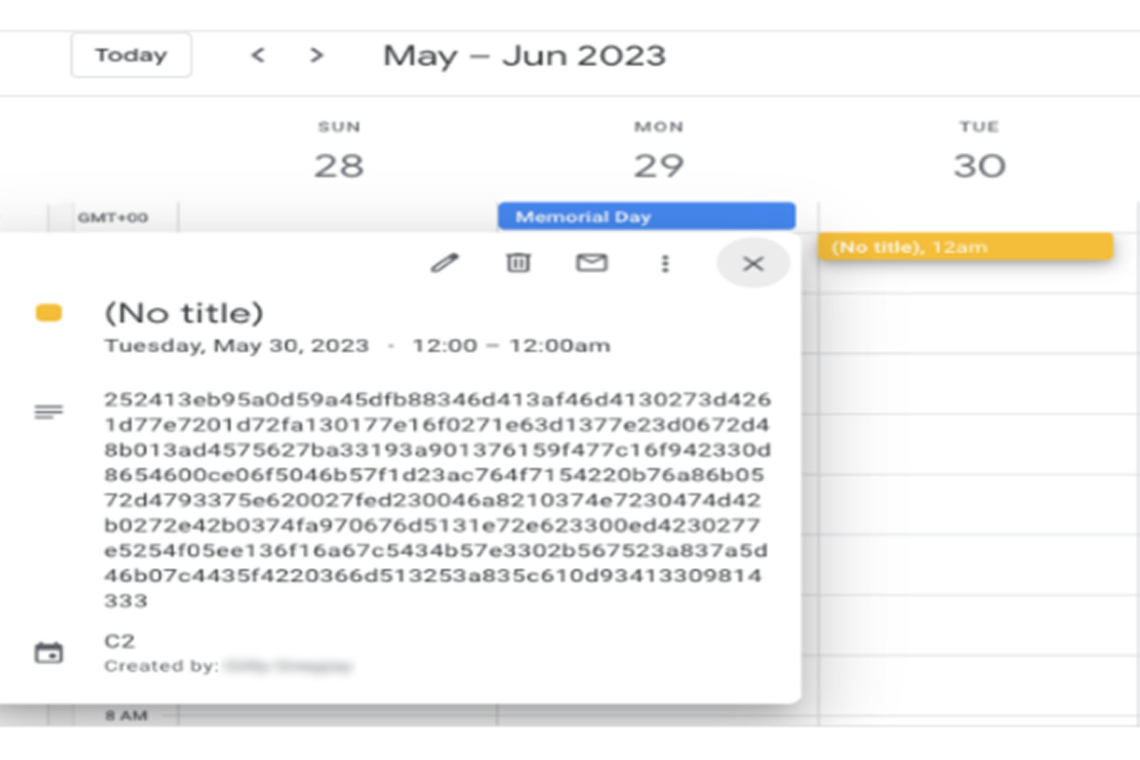
For command and control, TOUGHPROGRESS creates hidden events on specific hardcoded dates in Google Calendar. It encrypts stolen data and commands using XOR keys and compresses messages with LZNT1. Commands are embedded in event descriptions, which the malware retrieves and decrypts before executing on the infected system. Results from executed commands are encrypted and sent back as new calendar events, turning Google Calendar into a covert communication channel.
To counter the campaign, Google developed custom detection fingerprints to identify and take down attacker-controlled calendars. They also terminated the attacker-controlled Google Workspace projects that supported the malware’s infrastructure. Additionally, Google updated file detections and added malicious domains and URLs to the Google Safe Browsing blocklist.
Google GTIG and Mandiant Consulting have notified affected organizations and provided TOUGHPROGRESS network logs and threat intelligence to assist in detection and response efforts.
Found this article interesting? Follow us on X(Twitter) ,Threads and FaceBook to read more exclusive content we post.