Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered a new cryptojacking campaign targeting publicly accessible DevOps web servers, including those related to Docker, Gitea, HashiCorp Consul,
and Nomad. These attacks are designed to illicitly mine cryptocurrencies by exploiting various known vulnerabilities and misconfigurations in these systems.
The cloud security firm Wiz, which is monitoring this activity under the name JINX-0132, explained that attackers are taking advantage of multiple misconfigurations and weaknesses to deploy cryptocurrency mining software. Notably, this campaign appears to be the first publicly documented case of Nomad misconfigurations being exploited as a vector for attacks in the wild, according to researchers Gili Tikochinski, Danielle Aminov, and Merav Bar.
One distinct aspect of these attacks is that the threat actors are using legitimate tools downloaded directly from GitHub repositories instead of relying on their own infrastructure for staging. This approach seems to be a deliberate tactic to complicate efforts to trace the attacks back to their source.
JINX-0132 has successfully compromised Nomad instances that manage hundreds of clients. The combined computing power of these clients, measured in CPU and RAM resources, could cost tens of thousands of dollars monthly if properly paid for. This highlights the significant amount of processing power being hijacked for cryptomining. Exploiting Docker API instances is a common method in such attacks. Just recently, cybersecurity firm Kaspersky revealed that attackers are targeting misconfigured Docker API instances to recruit them into cryptocurrency mining botnets.
Exposed Docker API instances allow attackers to run malicious code by launching containers that either mount the host file system or run cryptocurrency mining images. This is done through standard Docker endpoints such as "/containers/create" and "/containers/{id}/start."
In addition, Wiz researchers noted that attackers are exploiting either vulnerabilities (such as CVE-2020-14144) or misconfigurations in Gitea, an open-source tool for hosting Git repositories, to gain initial access to targets. Publicly exposed Gitea instances are vulnerable to remote code execution if the attacker controls a user account with permission to create git hooks, the instance is running version 1.4.0, or if the installation page remains unlocked (INSTALL_LOCK=false).
Similarly, HashiCorp Consul can be exploited for arbitrary code execution if improperly configured. If the system allows any remote user to register services and define health checks, these checks can include bash commands executed by the registered agent. In this campaign, JINX-0132 abused this feature to add malicious checks that run mining software. The attackers added multiple services with random names whose true purpose was to download and execute the XMRig miner.
JINX-0132 has also been observed exploiting misconfigurations in publicly accessible Nomad server APIs. The attackers created multiple jobs on compromised hosts that download and run the XMRig miner from GitHub. These attacks rely on the fact that Nomad is not secure by default, allowing unrestricted server API access which is equivalent to remote code execution on the server and its connected nodes.
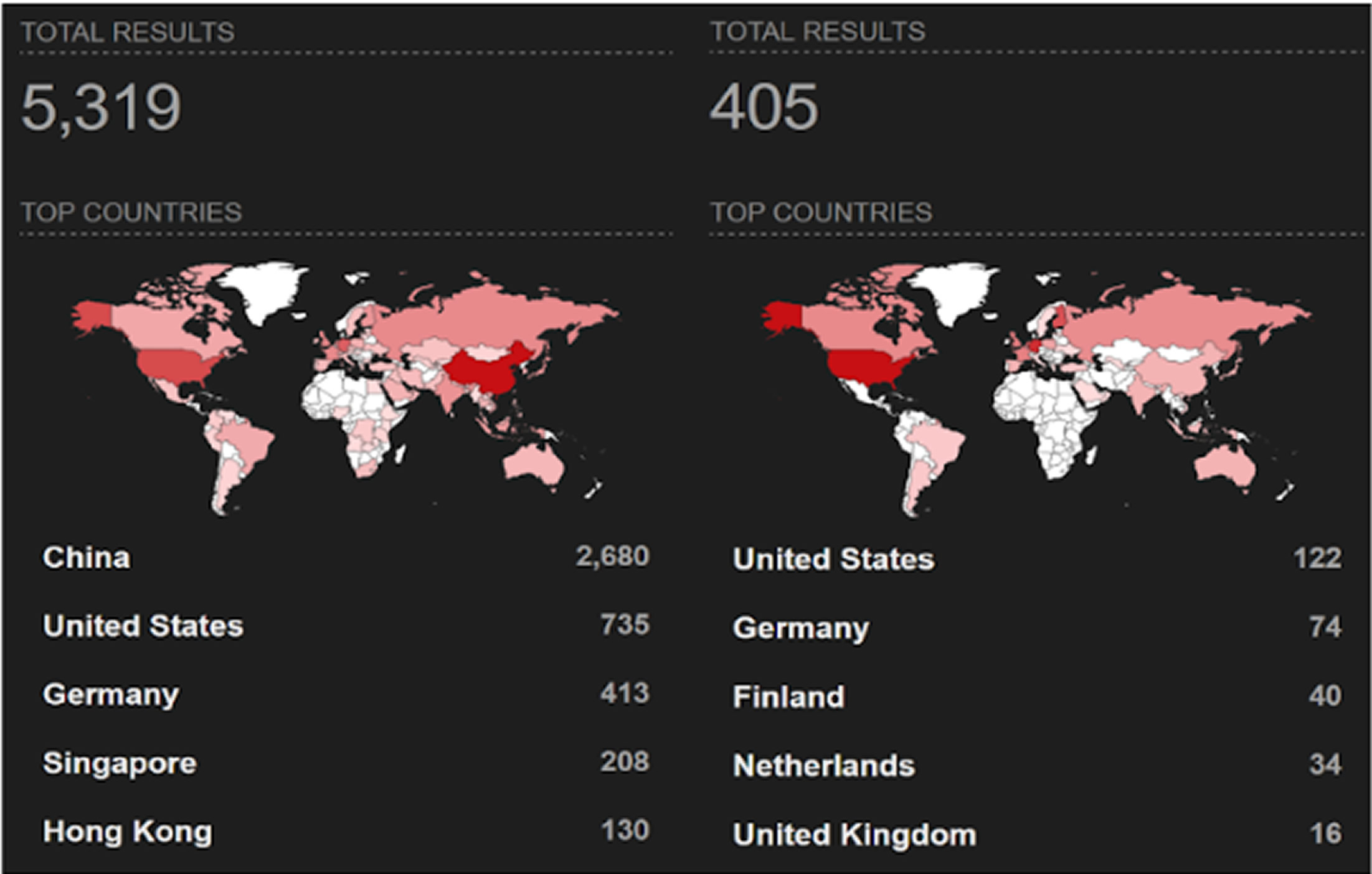
According to data from Shodan, there are over 5,300 exposed Consul servers and more than 400 exposed Nomad servers worldwide. Most of these exposed servers are located in countries such as China, the United States, Germany, Singapore, Finland, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom.
Separately, cybersecurity company Sysdig disclosed a malware campaign targeting both Linux and Windows systems by exploiting a misconfigured system hosting Open WebUI. This campaign involves uploading an artificial intelligence-generated Python script that ultimately delivers cryptocurrency miners.
The Open WebUI system was exposed to the internet, allowing anyone to execute commands. This misconfiguration is well-known among attackers who actively scan for such vulnerable systems. After discovering the exposed system, attackers used Open WebUI Tools, a plugin system designed to enhance large language model capabilities by uploading Python scripts. Once uploaded, the malicious Python code was executed.
Sysdig explained that the Python script downloads and runs cryptocurrency miners such as T-Rex and XMRig, creates a systemd service for persistence, and uses a Discord webhook for command and control communications. The malware employs libraries like processhider and argvhider to conceal the mining process on Linux, helping it evade detection. On Windows systems, the attack also deploys the Java Development Kit to run a JAR file ("application-ref.jar") downloaded from a suspicious IP address. This JAR file serves as a loader for a secondary JAR payload.
The attack concludes by executing two files, "INT_D.DAT" and "INT_J.DAT," with the latter designed to steal credentials from Discord and cryptocurrency wallet extensions installed in the Google Chrome browser.
Sysdig estimates that more than 17,000 Open WebUI instances are accessible on the internet, although it is unclear how many of these are misconfigured or vulnerable.
The researchers emphasized that accidental misconfigurations exposing systems like Open WebUI to the internet remain a serious security concern. This campaign targeted both Linux and Windows environments, with the Windows variant including advanced credential stealing and evasion techniques.
Found this article interesting? Follow us on X(Twitter) ,Threads and FaceBook to read more exclusive content we post.



