Two high-severity security vulnerabilities have been identified in the ruby-saml library, an open-source implementation
f the Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) used for authentication and authorization. These vulnerabilities could enable malicious actors to bypass SAML authentication protections, potentially leading to unauthorized access to sensitive systems and services.
SAML is a widely used XML-based open standard that facilitates single sign-on (SSO) functionality, allowing users to authenticate once and gain access to multiple applications without needing to re-enter credentials. Organizations across various industries rely on SAML for secure authentication, making any vulnerabilities within its implementation a serious concern.
The security flaws, tracked as CVE-2025-25291 and CVE-2025-25292, carry a CVSS severity score of 8.8 out of 10, highlighting their potential impact. The affected versions of the ruby-saml library include:
- Versions below 1.12.4
- Versions from 1.13.0 to below 1.18.0
Both vulnerabilities stem from the way two XML parsing libraries, REXML and Nokogiri, interpret XML differently. This discrepancy in parsing behavior can result in inconsistent document structures, creating an opportunity for attackers to execute a Signature Wrapping attack, which ultimately enables authentication bypass.
Exploiting the Vulnerabilities: How Attackers Can Bypass Authentication
The core issue arises from the way digital signatures are processed within the ruby-saml library. Attackers who possess a single valid signature—created using the key employed to validate SAML responses or assertions—can manipulate the SAML assertions to forge authentication credentials. This effectively allows them to log in as any user, including high-privilege accounts, without requiring the actual credentials of the target user.
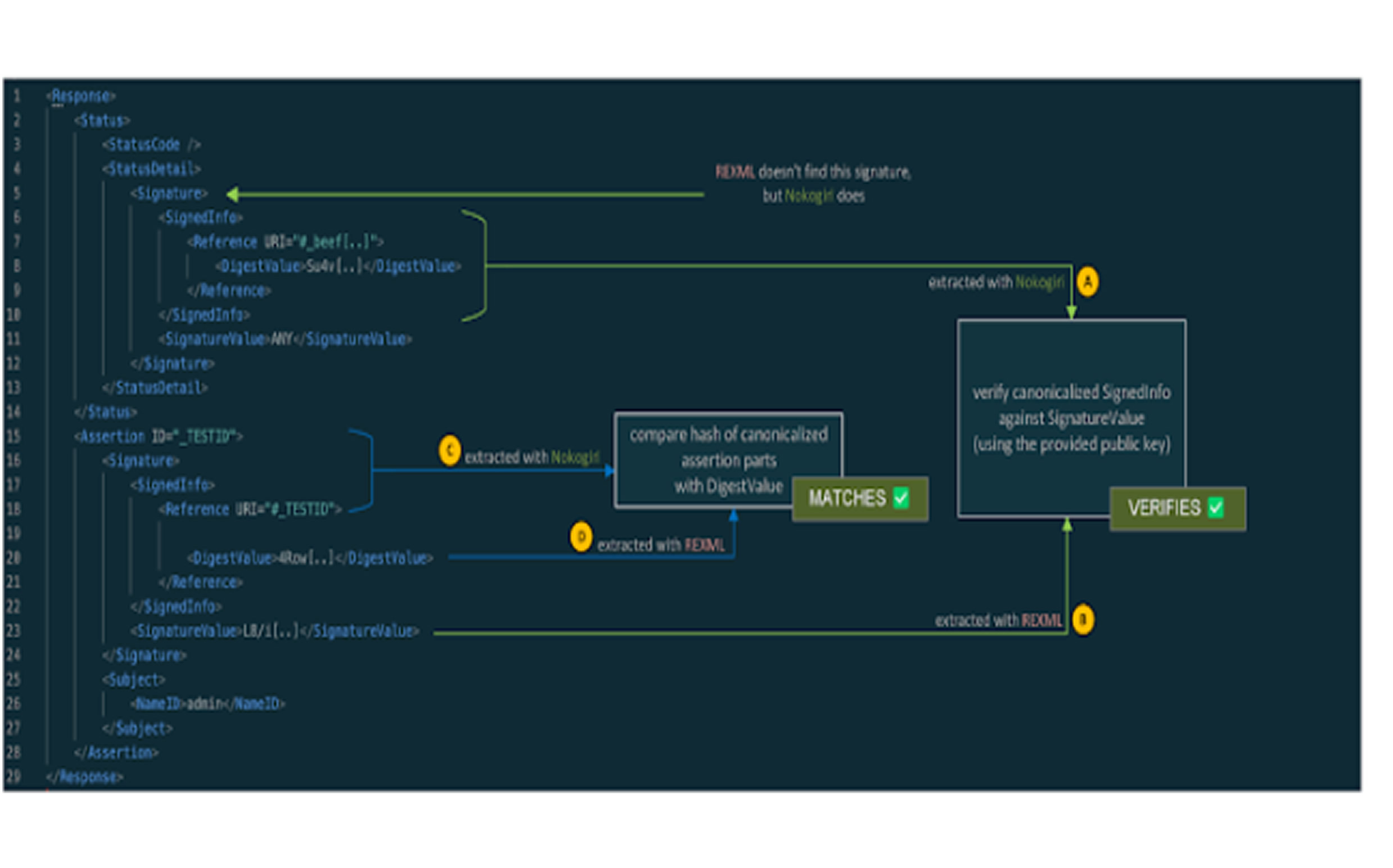
Microsoft-owned GitHub Security Lab, which discovered and reported the flaws in November 2024, emphasized that the issue results from a "disconnect" between hash verification and signature verification. This disparity enables attackers to exploit the parser differential, crafting malicious SAML assertions that pass verification despite being unauthorized.
"Attackers who are in possession of a single valid signature that was created with the key used to validate SAML responses or assertions of the targeted organization can use it to construct SAML assertions themselves and are in turn able to log in as any user," explained Peter Stöckli, a security researcher at GitHub.
Additional Security Risks: Remote Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attack
In addition to the authentication bypass vulnerabilities, another flaw, CVE-2025-25293, was identified within the ruby-saml library. This vulnerability, which has a CVSS score of 7.7, poses a risk of remote denial-of-service (DoS) attacks when handling compressed SAML responses. Attackers could exploit this flaw to overwhelm authentication services, potentially disrupting access to critical applications and services.
Patch and Mitigation Recommendations
To address these vulnerabilities, the maintainers of ruby-saml have released patched versions:
- 1.12.4
- 1.18.0
Users and organizations relying on ruby-saml for authentication are strongly encouraged to update to one of these secure versions immediately to protect their systems from potential exploitation.
Ongoing Security Challenges in SAML Implementations
This discovery comes just months after a previous critical vulnerability, CVE-2024-45409, was identified in GitLab and ruby-saml. That flaw, which carried a CVSS score of 10.0, also led to an authentication bypass risk, underscoring the ongoing security challenges faced by organizations that depend on SAML-based authentication.
Given the widespread use of SAML in enterprise security environments, security teams should remain vigilant and ensure that authentication mechanisms are regularly updated and thoroughly tested for weaknesses. Organizations should also implement additional security measures such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and strict access controls to minimize the risk of unauthorized access due to authentication bypass exploits.
By staying proactive in addressing vulnerabilities and updating affected software promptly, organizations can better defend against emerging threats targeting authentication protocols like SAML.


