The recent cascading supply chain attack, which ultimately affected users of the "tj-actions/changed-files" GitHub
Action and notably targeted Coinbase, has now been traced back to an earlier breach involving the open-source static analysis tool SpotBugs. According to Palo Alto Networks' Unit 42, the attackers exploited vulnerabilities in SpotBugs’ GitHub Actions workflow to gain initial access, setting the stage for a broader campaign that spanned multiple projects.
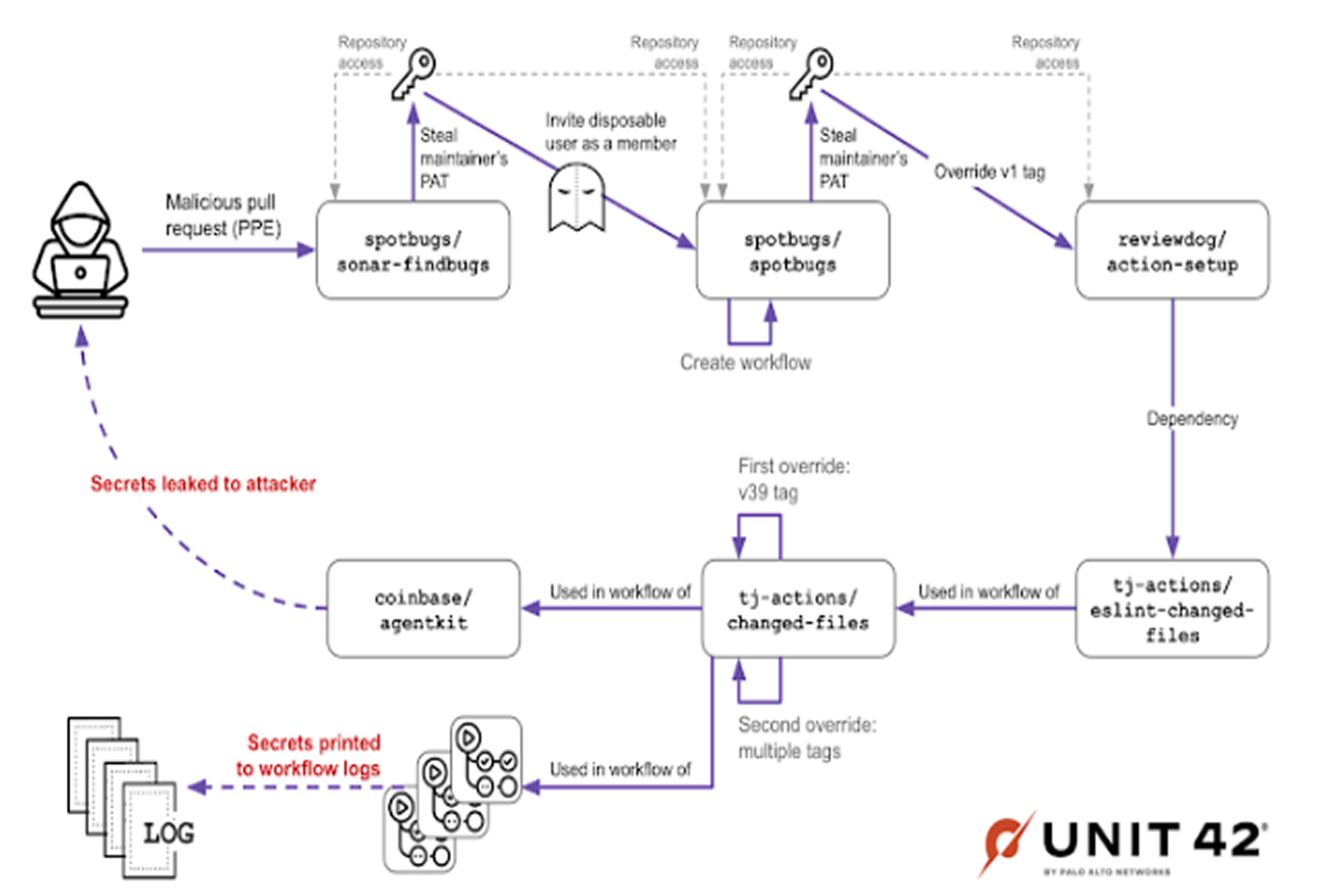
The breach began when the attackers managed to compromise a personal access token (PAT) belonging to a SpotBugs maintainer. This was achieved by exploiting a GitHub Actions workflow in the “spotbugs/sonar-findbugs” repository. The attackers submitted a malicious pull request using the “pull_request_target” trigger, which allowed them to execute code with elevated privileges and access repository secrets, including the maintainer’s PAT.
With access to the compromised PAT, the attackers were able to laterally move from the SpotBugs repository to another high-profile project, reviewdog. This movement was possible because the same PAT had access permissions for both “spotbugs/spotbugs” and “reviewdog/action-setup.” Once inside the reviewdog project, the attackers introduced a malicious version of the “reviewdog/action-setup” GitHub Action, which was later pulled in by “tj-actions/eslint-changed-files,” and by extension, impacted “tj-actions/changed-files.”
The malicious activity appears to have started as early as November 2024, but the attack on Coinbase didn’t take place until March 2025. It is believed that the threat actors strategically delayed their actions, monitoring repositories that depended on the compromised GitHub Action to wait for a valuable target.
An important development occurred on March 11, 2025, when the user “jurkaofavak”—controlled by the attackers—was invited to join the SpotBugs repository. This move gave them further access and enabled the poisoning of the project’s GitHub Actions environment. Notably, this invitation was made using the same PAT that had previously been leaked due to the poisoned pipeline execution (PPE) vulnerability exploited in December.
The attack highlights a significant weakness in how secrets and permissions are handled in GitHub Actions workflows. Specifically, the misuse of the “pull_request_target” trigger allowed the attackers to extract sensitive credentials from a forked repository. The SpotBugs maintainer has since rotated all tokens and access credentials in response to the breach.
Despite uncovering much of the attack chain, one lingering question remains: why the attackers waited for nearly three months between acquiring the PAT and using it. Investigators speculate that the attackers were monitoring dependent projects to strike at the most impactful time ultimately using their access to launch a sophisticated and high-value attack against Coinbase and others in the open-source ecosystem.


