A recently patched vulnerability in macOS could have allowed attackers to bypass Transparency, Consent, and Control (TCC) protections and steal sensitive user data, including information cached by Apple Intelligence.
TCC is a privacy and security framework in macOS that regulates how applications access personal data, ensuring that apps follow strict permissions and data usage policies.
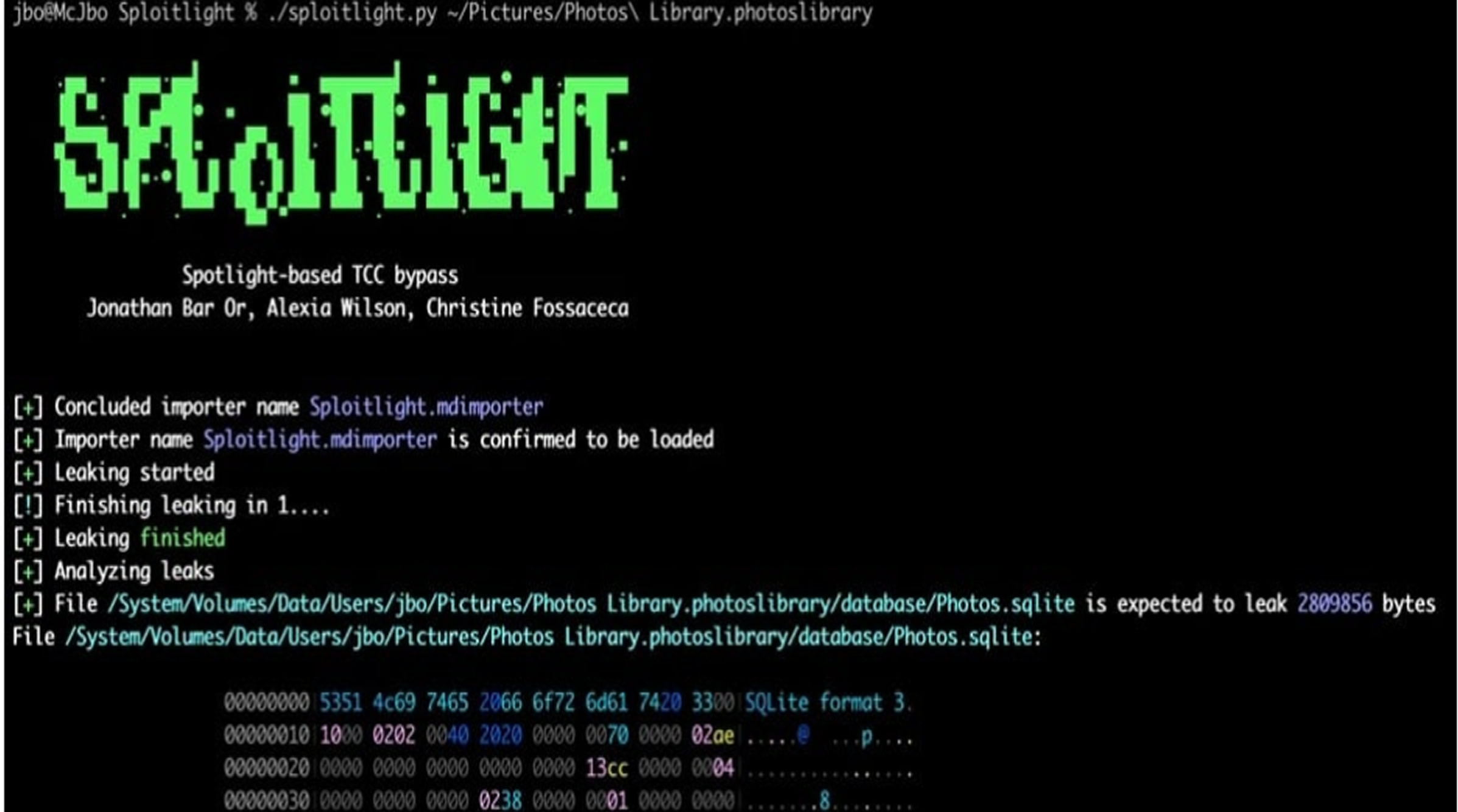
Apple addressed the flaw, identified as CVE-2025-31199, in macOS Sequoia 15.4 through a patch released in March that enhanced data redaction. The vulnerability, reported by Microsoft's Jonathan Bar Or, Alexia Wilson, and Christine Fossaceca, exploited the elevated privileges of Spotlight plugins to gain access to protected files.
Microsoft researchers demonstrated that attackers could leverage this weakness to gather data such as photo and video metadata, geolocation information, user activity, recognition data, and even deleted content. The vulnerability, dubbed “Sploitlight,” was described by Apple as a logging issue.
The researchers also noted that the vulnerability could be used to access information from devices linked to the same iCloud account, increasing the potential impact of an attack.
Since 2020, Apple has resolved multiple TCC bypass vulnerabilities, including those involving Time Machine mounts (CVE-2020-9771), environment variable poisoning (CVE-2020-9934), and bundle conclusion flaws (CVE-2021-30713). Microsoft had also previously identified TCC bypasses such as “powerdir” (CVE-2021-30970) and “HM-Surf.”
According to Microsoft, the Sploitlight vulnerability poses a greater threat because it can extract Apple Intelligence data and exploit iCloud-linked device connections, increasing the risk of remote exposure.
Microsoft has also discovered several other critical macOS flaws in recent years, including a System Integrity Protection (SIP) bypass named “Shrootless” (CVE-2021-30892), another SIP bypass called “Migraine” (CVE-2023-32369), the “Achilles” flaw (CVE-2022-42821) which bypasses Gatekeeper, and a 2024 SIP bypass (CVE-2024-44243) that allows installation of malicious kernel drivers using third-party extensions.
Found this article interesting? Follow us on X(Twitter) ,Threads and FaceBook to read more exclusive content we post.



