On Tuesday, Google announced that its large language model (LLM)-powered vulnerability detection system had identified a flaw in the SQLite open-source database engine before it could be exploited.
The vulnerability, labeled CVE-2025-6965 with a CVSS score of 7.2, is a memory corruption issue affecting all SQLite versions before 3.50.2. It was uncovered by Big Sleep, an AI agent developed through a collaboration between Google DeepMind and Google Project Zero.
According to SQLite project maintainers, “An attacker who can inject arbitrary SQL statements into an application might be able to cause an integer overflow, leading to reading beyond the bounds of an array.” Google classified the vulnerability as a high-risk security issue that was previously unknown to the public but had likely been discovered by threat actors. However, Google did not disclose who these actors were.
Kent Walker, President of Global Affairs at Google and Alphabet, said, “By combining threat intelligence with Big Sleep, we were able to anticipate that this vulnerability would be used imminently and prevent its exploitation in time.”
He added that this marks the first known instance of an AI agent successfully disrupting a potential attack before it could be carried out.
Big Sleep had also found another SQLite vulnerability in October 2024. That flaw was a stack buffer underflow issue that could have resulted in application crashes or even allowed arbitrary code execution.
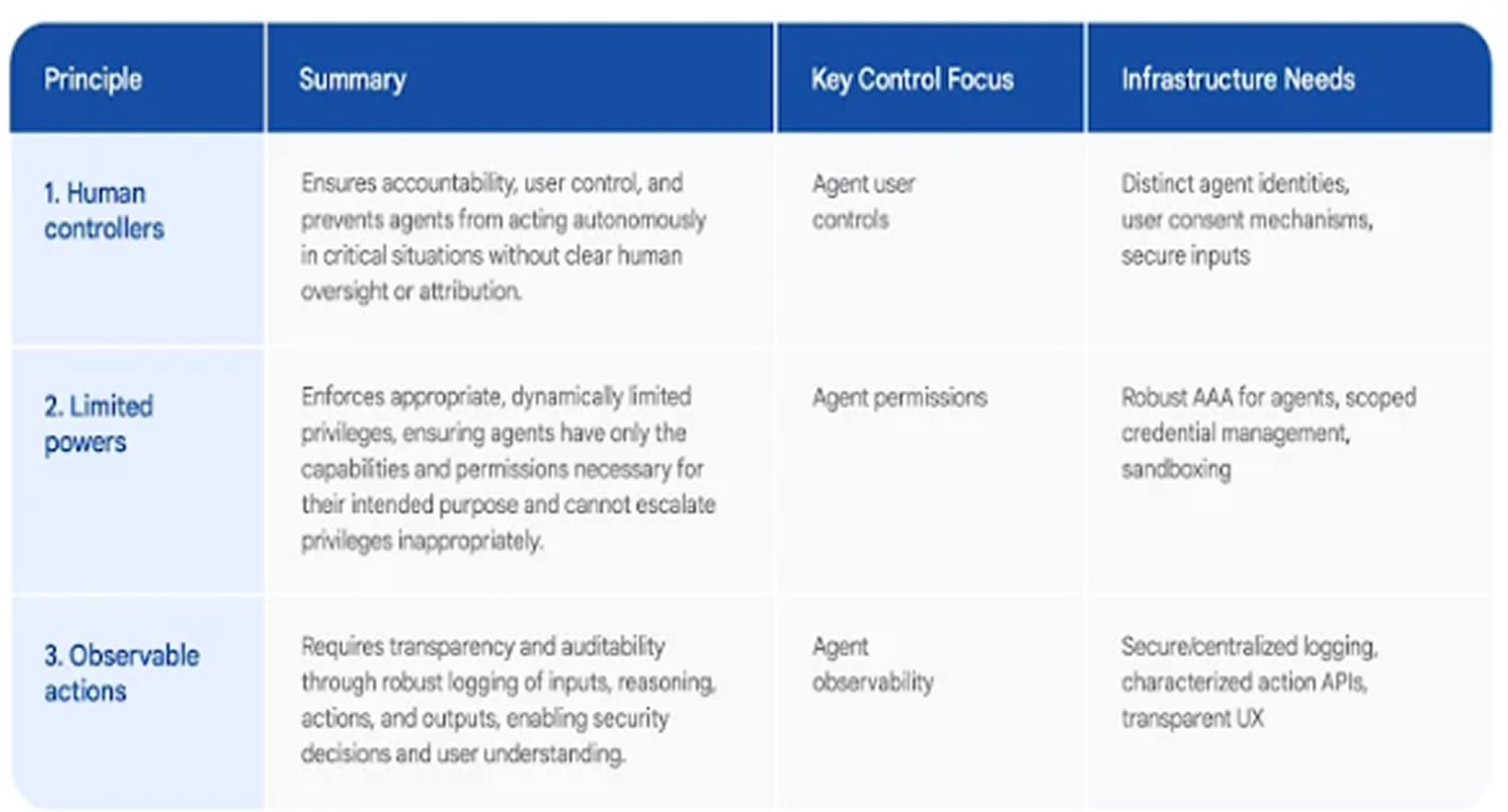
Alongside this achievement, Google published a white paper outlining best practices for securing AI agents. The document emphasizes the importance of keeping human oversight, limiting AI capabilities to prevent unintended behavior or data exposure, and ensuring that AI actions remain observable.
Google researchers Santiago (Sal) Díaz, Christoph Kern, and Kara Olive explained that traditional security measures alone may not provide the flexibility needed for AI agents, while relying entirely on the AI’s own reasoning is also risky. Current LLMs are still vulnerable to manipulation tactics like prompt injection and do not yet offer strong security guarantees.
To address this, Google has adopted a hybrid defense-in-depth strategy. This approach combines traditional rule-based controls with dynamic, AI-based defenses to build strong security barriers around AI agent environments. These protections are designed to prevent harmful outcomes, such as actions caused by prompt injection or other unexpected inputs.
According to Google, “This layered approach acts as a safeguard in case an AI agent’s reasoning process is compromised. It ensures that both static rules and intelligent decision-making work together to maintain safety and control.”
Found this article interesting? Follow us on X(Twitter) ,Threads and FaceBook to read more exclusive content we post.



