A sophisticated cyber campaign is targeting macOS users with a potent information stealer called Odyssey. The malware is being distributed through a fraudulent website that imitates the official Microsoft Teams download page.
The attack, identified by researchers at CloudSEK’s TRIAD, uses a social engineering technique known as a “Clickfix” attack. Victims are lured to a fake Microsoft security verification page and are instructed to copy and paste a command into their Terminal to resolve an issue. Although the command appears harmless, the "Copy" button actually places a malicious script on the user’s clipboard. When the victim executes this command, they unwittingly launch the Odyssey stealer.
This campaign is a tactical evolution of a similar attack that used a fake TradingView site. By impersonating a widely-used enterprise application like Microsoft Teams, the attackers are now able to target a much broader audience.
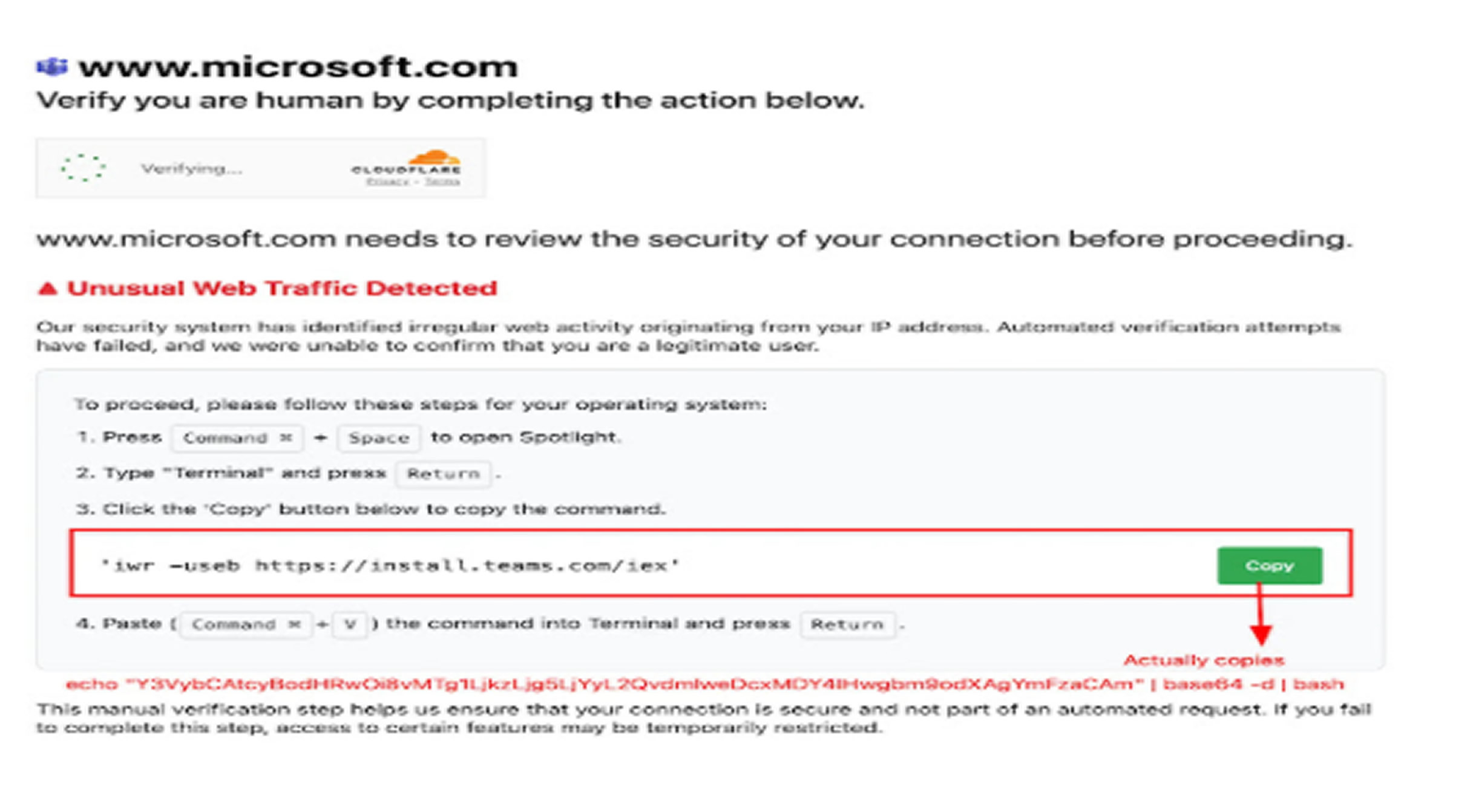
How the Odyssey Malware Works
Once the malware is active, it takes several malicious steps:
- Credential Theft: The script repeatedly prompts the user for their password via a fake dialog box. After the password is entered, the malware steals the macOS login keychain and the Chrome browser’s keychain.
- Data Collection: Odyssey sweeps the system for a wide range of information, including Apple Notes, Safari browser data, and artifacts from Chromium and Firefox browsers. It also specifically targets data from password managers and cryptocurrency wallet extensions like MetaMask. It copies data from numerous desktop crypto wallets like Electrum and Exodus, and searches for personal files with specific extensions on the user's Desktop and Documents folders.
- Data Exfiltration: All the collected data is compressed into a single zip file and sent to a command-and-control server.
- Persistence and Tampering: The malware establishes a persistent backdoor by creating a service that runs automatically at startup. In a particularly bold move, it replaces the legitimate Ledger Live application with a trojanized version downloaded from its server, giving the attackers direct control over the user’s crypto hardware wallet interactions.
Mitigating the Threat
The consequences of this attack can be severe, leading to data breaches and significant financial loss. To protect against this threat, experts recommend the following actions:
- Network Monitoring: Block traffic to the known command-and-control server's IP address and monitor for suspicious outbound requests.
- Endpoint Security: Regularly check system folders for unusual files and look for recent, unexpected script executions.
- User Vigilance: Be extremely cautious of any website that asks you to run commands in your Terminal. Always verify the authenticity of a download page before proceeding.
- Incident Response: If you suspect an infection, immediately change all critical passwords from a clean system. It is also advised to remove the trojanized Ledger Live application and consider a full system wipe to ensure the malware is completely gone.
Found this article interesting? Follow us on X(Twitter) ,Threads and FaceBook to read more exclusive content we post.



