North Korea-linked cyber threat actors have been observed weaponizing fake job recruitment schemes to infiltrate the systems of software developers
and IT professionals, deploying updated versions of BeaverTail and InvisibleFerret—two advanced malware strains designed for multi-platform espionage and financial theft.
The ongoing campaign, tracked as CL-STA-0240 and referred to as Contagious Interview, was first disclosed by Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 in November 2023. Despite its exposure, recent evidence suggests the attackers have refined their tactics and are still successfully compromising victims under the guise of job recruitment processes.
Social Engineering: A High-Stakes Cyber Espionage Tactic
The modus operandi of the Contagious Interview campaign revolves around highly targeted social engineering:
Impersonation of recruiters: The adversaries pose as hiring managers or technical recruiters on job search platforms such as LinkedIn, Indeed, or specialized developer forums.
Engagement with software developers: They engage with software engineers, DevOps professionals, and IT specialists, luring them into a fraudulent job application process.
Weaponized coding assignments & interview tools: Victims are encouraged to download what they believe is an assignment file or a legitimate video conferencing application to proceed with the interview.
Deployment of malicious software: These applications contain malware-laden payloads, ultimately infecting both Windows and macOS devices.
"Even though the campaign has been publicly reported and analyzed, social engineering techniques—like impersonating recruiters—remain highly effective," said Assaf Dahan, Director of Threat Research at Unit 42. "By exploiting trust and urgency in professional settings, these attackers have created a reliable method of gaining access to victims' devices."
Multi-Stage Attack Chain: From Initial Infection to Full Compromise
The infection process follows a layered, multi-stage deployment mechanism, leveraging cross-platform compatibility to maximize impact.
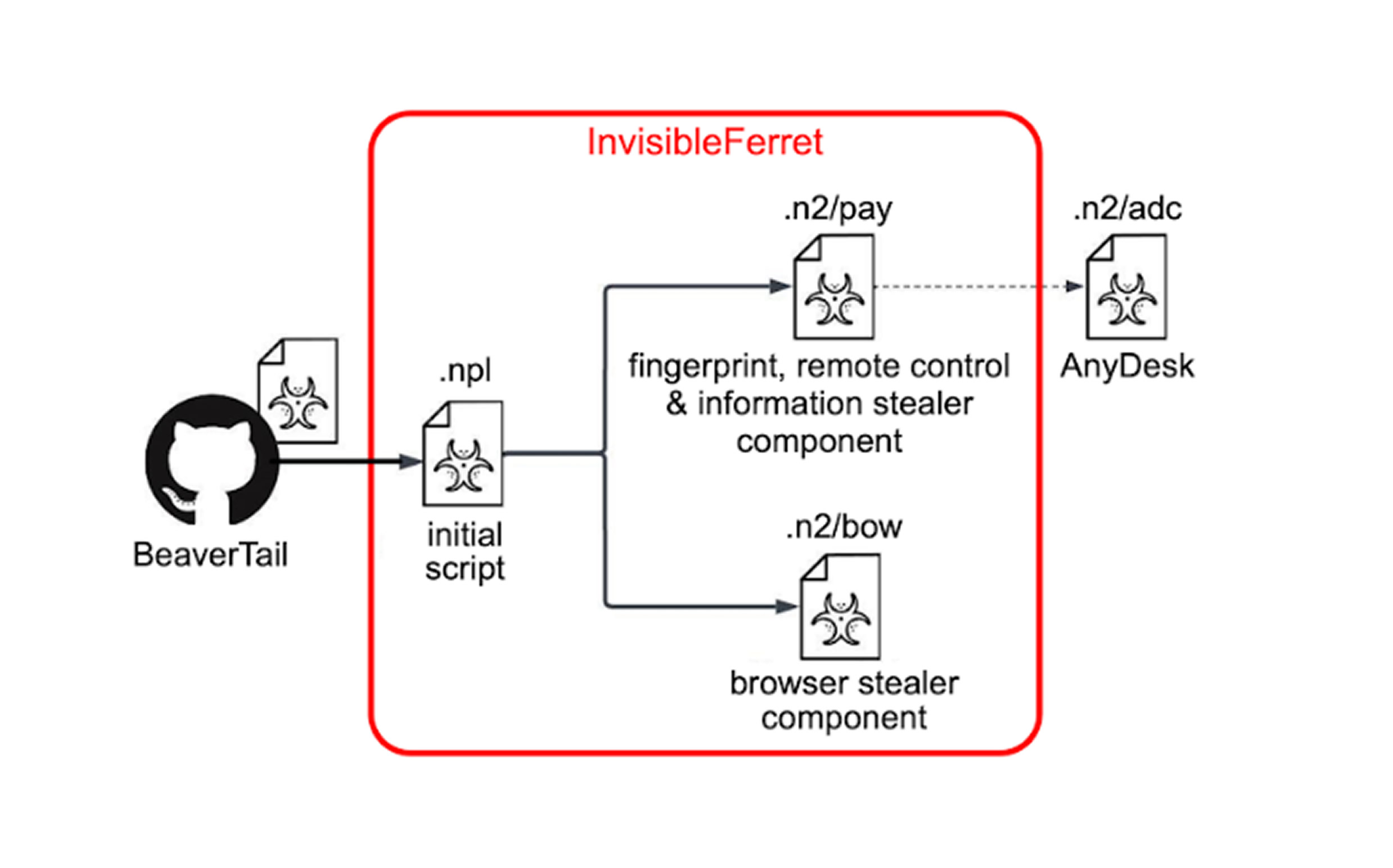
1. Initial Payload – BeaverTail Malware
The first-stage malware, BeaverTail, functions as a downloader and information stealer, supporting both Windows and macOS environments. Originally developed in Python, its latest iteration is now rewritten using the Qt framework, significantly improving its stealth capabilities.
BeaverTail Capabilities:
Steals browser credentials: Extracts saved passwords, cookies, and autofill data from victims' browsers.
Harvests cryptocurrency wallets: Capable of targeting 13 different cryptocurrency wallets, suggesting a financial crime motivation.
Exfiltrates system metadata: Sends details about the infected system to a remote command-and-control (C2) server.
Downloads & executes secondary payloads: Acts as a loader for InvisibleFerret, a sophisticated backdoor.
2. Secondary Payload – InvisibleFerret Backdoor
Once BeaverTail successfully infiltrates the system, it proceeds to download and execute InvisibleFerret, which is Python-based and designed for long-term persistence.
InvisibleFerret Capabilities:
Remote Host Fingerprinting: Collects detailed system information, including hardware details, OS version, and active processes.
Keylogging & Credential Theft: Logs keystrokes to capture login credentials and sensitive user data.
Financial Data Theft: Extracts stored credit card information from browsers.
Lateral Movement & Remote Control: Provides attackers with full access to the infected machine for executing further payloads.
AnyDesk Deployment: Installs and configures AnyDesk, a legitimate remote desktop tool, to enable persistence and remote manipulation of the victim’s device.
Use of Fake Video Conferencing Applications
Security researchers Patrick Wardle and Group-IB discovered that the attackers impersonated legitimate video conferencing tools, such as:
MiroTalk – An open-source web-based video conferencing solution.
FreeConference.com – A real online meeting platform.
These fake applications were developed using the Qt framework, allowing cross-compilation for both Windows and macOS. By disguising malware as trusted communication tools, the attackers significantly lowered the likelihood of detection, ensuring victims executed the malicious software under the assumption that it was necessary for their job interview.
Despite being publicly exposed in 2023, the CL-STA-0240 campaign has remained largely unchanged due to its continued success. There are three primary reasons why this approach continues to yield results:
Persistent Effectiveness of Social Engineering
Tech job seekers may overlook basic security practices when under pressure to secure a job offer.
Many individuals trust recruiters and are unaware of these advanced tactics.
Cross-Platform Malware Development
The shift to Qt-based malware has enabled seamless infection across both macOS and Windows systems, expanding the potential victim pool.
Financially Motivated Cybercrime
North Korean cyber units have a long history of conducting financially driven operations to fund the DPRK regime.
The theft of cryptocurrency wallets and credit card data suggests a strong cybercrime-for-profit motivation alongside espionage.
Mitigation Strategies: How to Protect Against Contagious Interview Attacks
Given the sophistication and effectiveness of this campaign, security experts recommend implementing the following protective measures:
1. Cyber Hygiene for Job Seekers
Verify recruiter identities: Cross-check recruiters on company websites or LinkedIn before engaging.
Avoid downloading unknown software: Always verify interview-related software before installation.
Use a sandbox environment: Execute unfamiliar files in a controlled virtual machine to analyze potential threats.
2. Endpoint Security & Network Defenses
Deploy Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR): Advanced security solutions can detect and flag malicious behavioral patterns associated with BeaverTail and InvisibleFerret.
Monitor network traffic: Analyze outbound connections to identify unusual data exfiltration attempts.
Harden system configurations: Restrict PowerShell execution policies, enforce code-signing requirements, and limit installation privileges.
3. Secure Cryptocurrency Wallets & Credentials
Use hardware wallets: Store crypto funds in offline, hardware-based wallets to prevent software-based theft.
Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA): Protect all financial accounts with strong 2FA solutions.
Regularly audit stored credentials: Use password managers that do not save sensitive data in browsers.
The Contagious Interview campaign demonstrates how threat actors with ties to the DPRK regime are continuing to refine and successfully execute cyber-espionage and financial theft operations by leveraging social engineering, cross-platform malware development, and fake recruitment processes.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, organizations and individuals must remain vigilant against deceptive tactics, particularly within professional and employment-related settings. Implementing strong cybersecurity awareness, endpoint protection, and proactive monitoring will be key to mitigating these persistent nation-state-sponsored threats.


