New Malware Campaign Uses Social Engineering to Deploy r77 Rootkit
A recently identified malware campaign is exploiting social engineering tactics to distribute an open-source rootkit known as r77.
Tracked as OBSCURE#BAT by Securonix, the campaign allows attackers to maintain persistence and evade detection on infected systems. The identity of the threat actors behind the attack remains unknown.
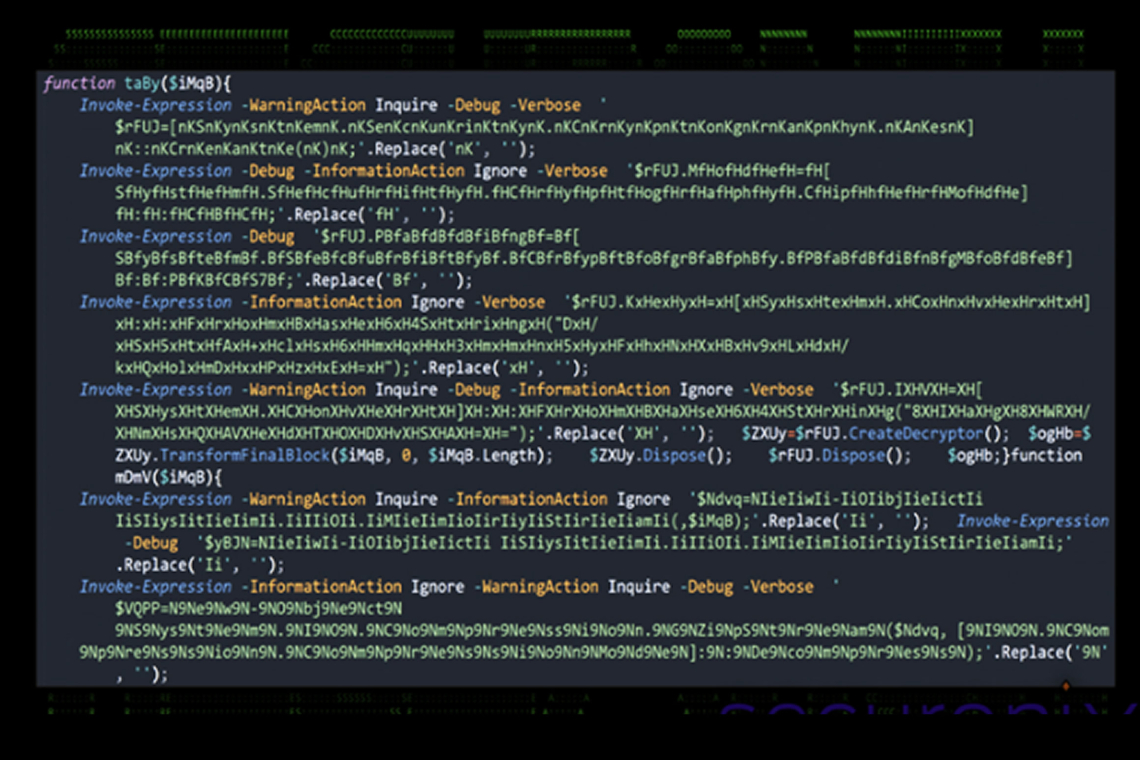
According to security researchers Den Iuzvyk and Tim Peck, the rootkit can conceal files, registry keys, and processes that start with a specific prefix. Attackers distribute the malware by disguising it as legitimate software downloads or through fake CAPTCHA scams.
The campaign primarily targets English-speaking users in the U.S., Canada, Germany, and the U.K. OBSCURE#BAT is named after the obfuscated Windows batch script that initiates the attack, executing PowerShell commands to deploy the rootkit in a multi-stage process.
Methods of Infection
Researchers identified two key methods used to lure victims into executing malicious batch scripts:
Fake Cloudflare CAPTCHA pages (ClickFix strategy) – Users are tricked into completing a fake verification step, which downloads the malware.
Disguised legitimate software downloads – The malware is advertised as well-known tools such as Tor Browser, VoIP software, and messaging clients via methods like malvertising and SEO poisoning.
Attack Execution & Evasion Techniques
Once a victim runs the malicious batch script, it:
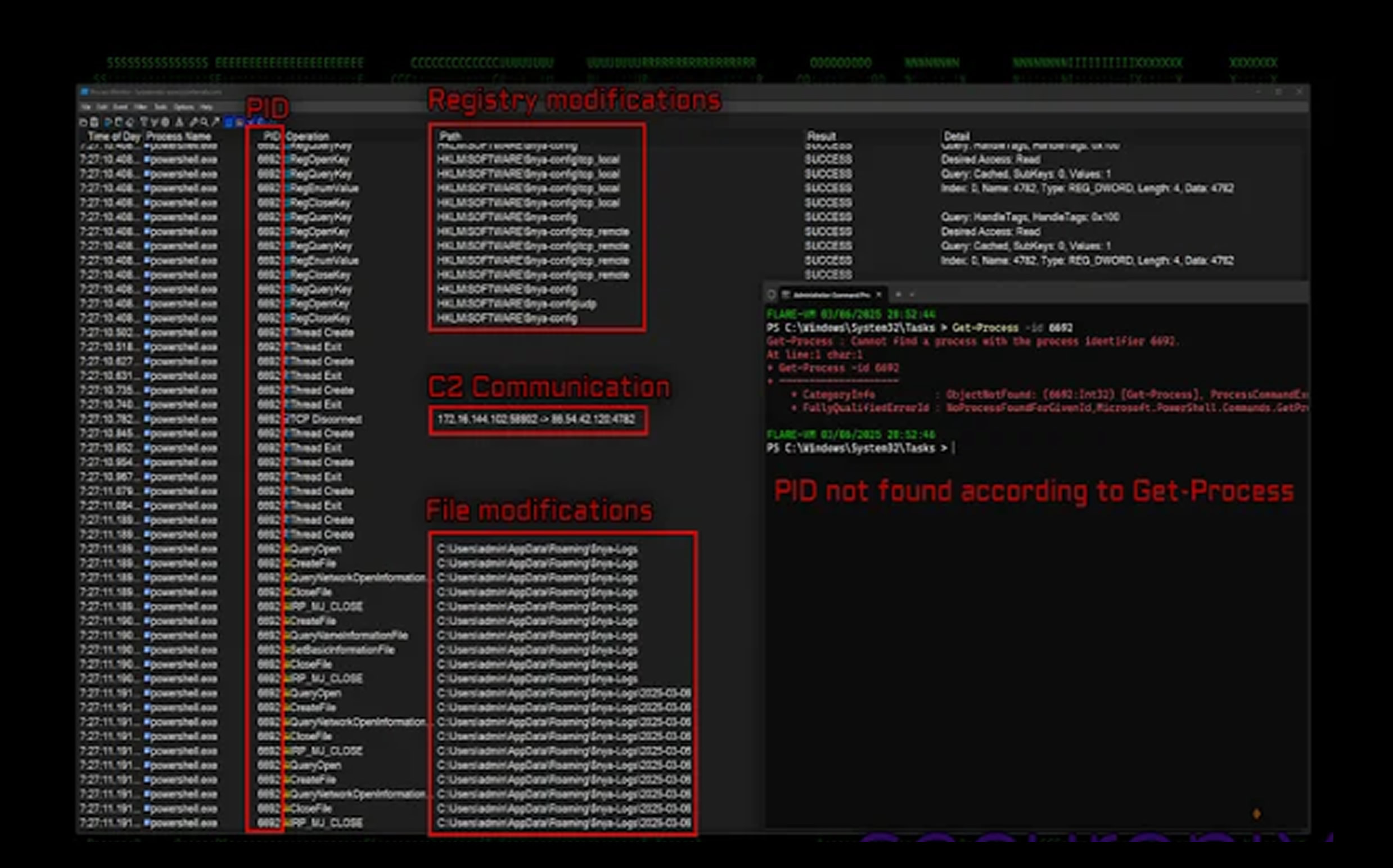
- Drops obfuscated scripts into the Windows Registry for stealthy execution.
- Creates scheduled tasks to maintain persistence.
- Registers a fake driver (ACPIx86.sys) to embed itself into the system.
- Uses a .NET payload with advanced obfuscation (control-flow manipulation, string encryption, and mixed-character function names) to evade detection.
- Employs AMSI patching to bypass antivirus software.
The final payload installs both a system-mode rootkit (ACPIx86.sys) and a user-mode rootkit (r77) in the Windows directory. These components ensure persistence by hiding files, processes, and registry keys that match a specific pattern.
Additionally, the malware monitors clipboard activity and command history, saving this information in hidden files likely for exfiltration.
Highly Evasive Attack Chain
OBSCURE#BAT employs multiple stealth techniques, including:
- API hooking to remain undetected.
- Process injection into system-critical processes like winlogon.exe to manipulate system behavior.
- Persistence mechanisms that survive system reboots.
These findings coincide with a separate Microsoft Copilot spoofing campaign uncovered by Cofense, where attackers use phishing emails to trick users into providing login credentials and 2FA codes.