A major vulnerability identified in ServiceNow’s platform, listed as CVE-2025-3648 and nicknamed “Count(er) Strike,” allows threat actors to extract sensitive data such as personally identifiable information (PII), login credentials, and financial records.
This high-severity issue leverages the record count feature on list pages by using enumeration techniques and query filters. It potentially affects all ServiceNow instances, placing hundreds of tables at risk. One of the most alarming aspects of the flaw is that it requires only minimal user privileges and can be exploited by low-level accounts, including those created through anonymous self-registration.
Understanding the Count(er) Strike Flaw
According to Varonis Threat Labs, the vulnerability targets ServiceNow’s Access Control List (ACL) mechanism. ACLs determine access using four criteria: required roles, security attribute conditions, data conditions, and script conditions. When a user is denied access based on roles or security attributes, the system shows a blank page with a security warning. However, when access is denied due to data or script conditions, ServiceNow still displays a message revealing the number of records hidden by security constraints.
This behavior unintentionally reveals useful information to attackers. Tables with weak or empty role and attribute requirements become vulnerable, allowing attackers to estimate data volumes and refine their queries.
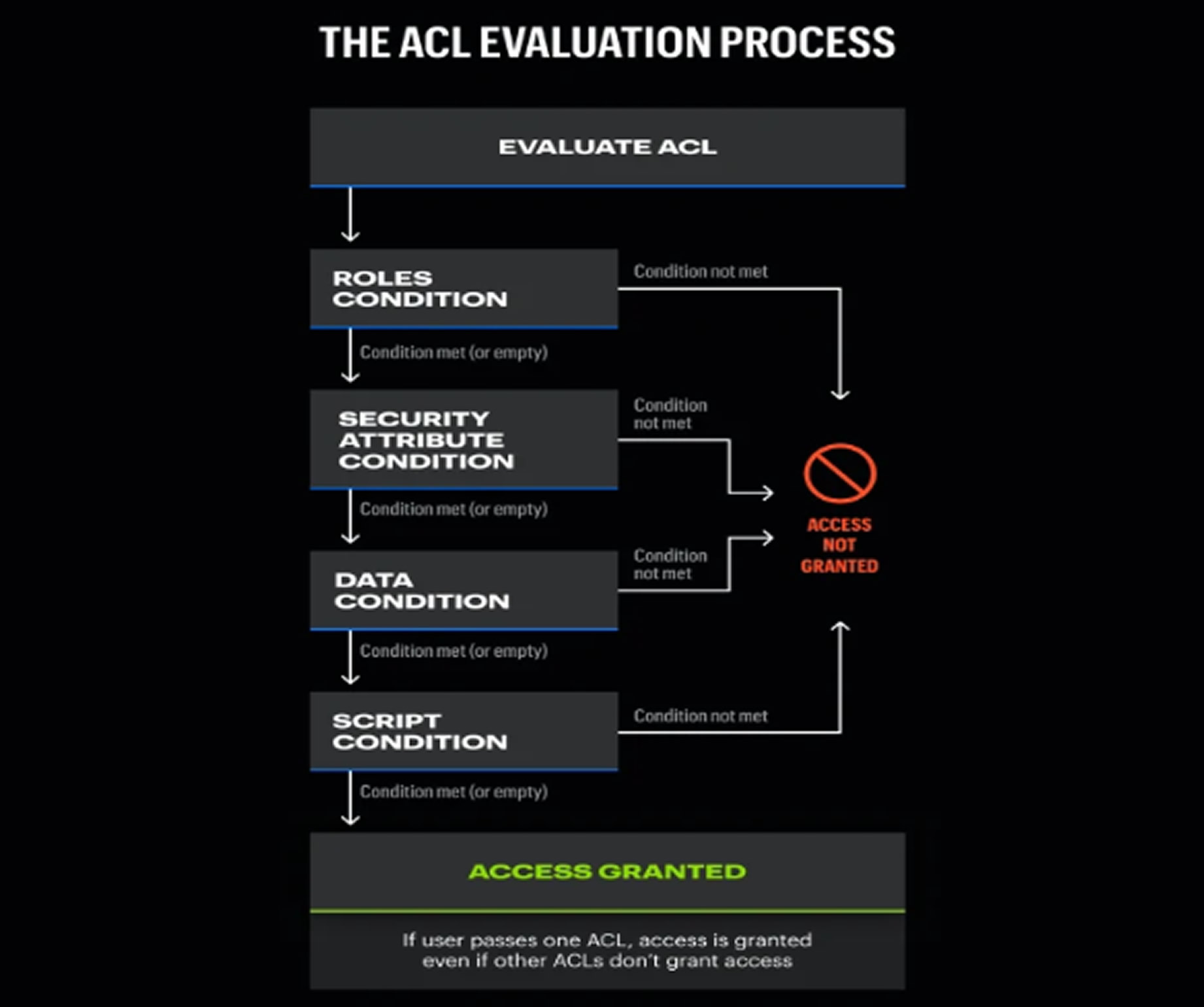
The issue affects several core ServiceNow modules, including IT Service Management (ITSM), Customer Service Management (CSM), and Human Resources Service Delivery (HRSD). Since ServiceNow is used by many Fortune 500 companies, the potential exposure spans a wide range of industries and sectors.
How Attackers Can Exploit the Flaw
The vulnerability can be exploited through URL manipulation using custom query parameters. For example, an attacker might use a parameter to filter records that begin with the letter “a.” The system responds with a record count embedded in the HTML, enabling the attacker to infer the existence and structure of data.
Using automated scripts, threat actors can repeat this process character by character to reconstruct full records. The risk increases further due to ServiceNow’s dot-walking feature, which enables queries across related tables, and the platform’s allowance for anonymous users to self-register and gain basic access.
What Has Been Done and What You Should Do
To resolve this issue, ServiceNow has implemented new access control capabilities. One key measure is the introduction of Query ACLs. These distinguish between two types of query actions: query_range, which includes higher-risk operators like STARTSWITH and CONTAINS, and query_match, which allows only safer operators such as EQUALS and NOT_EQUALS.
Additionally, new security data filters enhance protection by applying record-level restrictions based on user roles and attributes. These filters also suppress the previously exposed record count message, making it harder for attackers to use enumeration techniques.
Organizations using ServiceNow are strongly advised to review and update their ACL configurations across all instances. Special attention should be given to sensitive or regulated data stored in both standard and custom tables. Implementing the latest security controls is essential to prevent potential data exposure and maintain compliance.
Found this article interesting? Follow us on X(Twitter) ,Threads and FaceBook to read more exclusive content we post.



