A threat group known as UAT-6382, which communicates in Chinese, has been associated
with exploiting a now-fixed remote code execution vulnerability in Trimble Cityworks. This exploitation has been used to deploy Cobalt Strike and VShell.
According to Cisco Talos researchers Asheer Malhotra and Brandon White, UAT-6382 exploited the vulnerability CVE-2025-0944, performed system reconnaissance, and quickly installed several web shells and custom malware to secure long-term access. After breaching the system, the group appeared particularly focused on accessing infrastructure tied to utility management.
The campaign has been observed targeting enterprise networks of local governments in the United States since January 2025.
CVE-2025-0944, which carries a CVSS score of 8.6, is a deserialization vulnerability in Cityworks, a GIS-focused asset management platform. Exploiting this flaw could allow attackers to execute remote code. The vulnerability was patched and subsequently added to the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency's Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog in February 2025.
Trimble shared indicators of compromise (IoCs) indicating that the flaw had been used to deliver a Rust-based loader, which then executes Cobalt Strike and a Go-based remote access tool called VShell. These tools are designed to help attackers maintain persistent access to compromised networks.
Cisco Talos has labeled the Rust-based loader as TetraLoader. It was developed using MaLoader, a publicly available malware framework written in Simplified Chinese. Once the attackers successfully exploited the Cityworks application, they began by scanning and identifying the server. They then installed commonly used web shells such as AntSword, chinatso/Chopper, and Behinder, which are frequently leveraged by Chinese hacking groups.
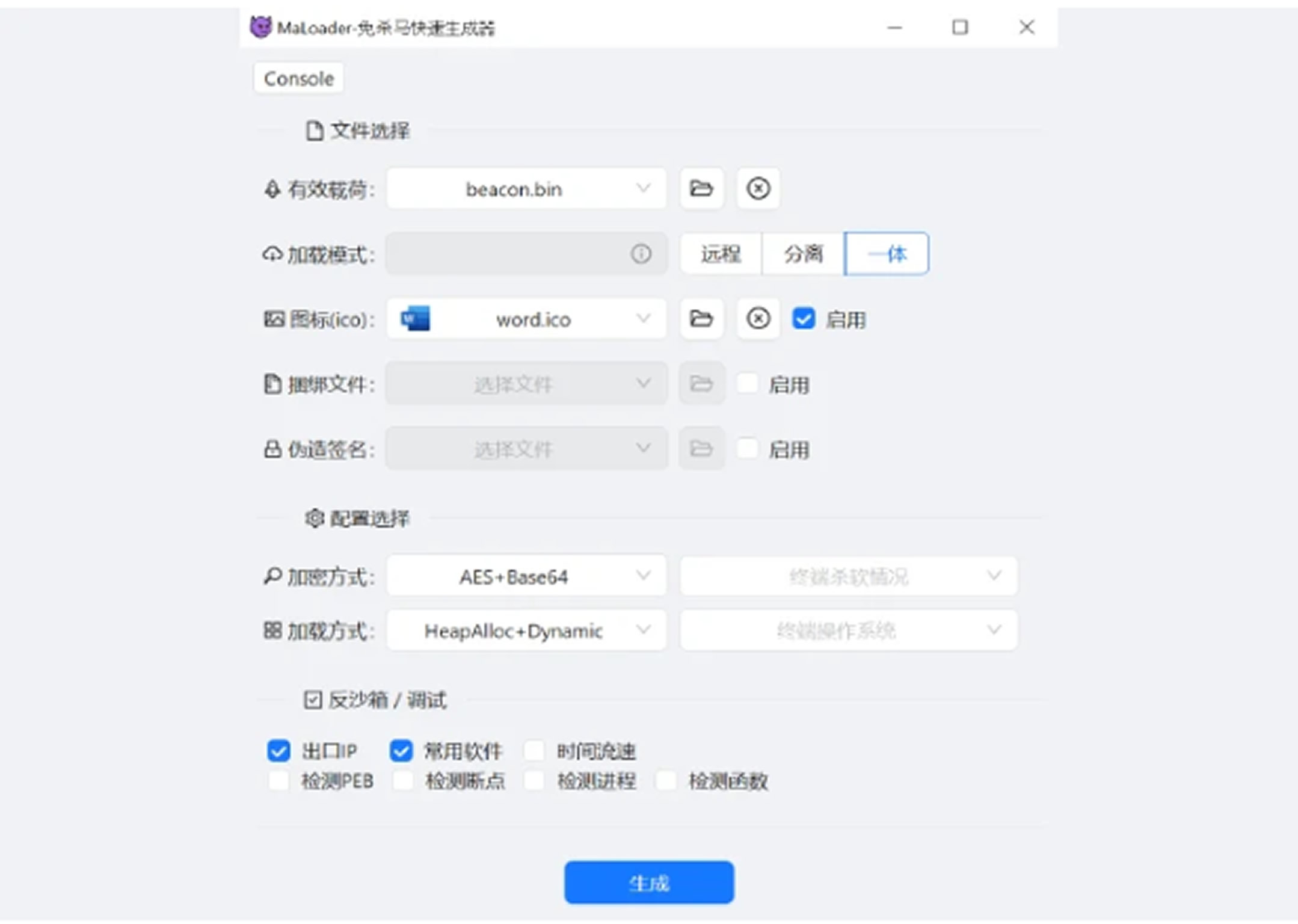
The researchers noted that UAT-6382 browsed through multiple directories on the targeted servers, looking for specific files of interest. These files were then moved to locations already compromised with web shells to simplify data exfiltration. The attackers also used PowerShell to download and install additional backdoors across infected systems.
Found this article interesting? Follow us on X(Twitter) ,Threads and FaceBook to read more exclusive content we post.



