A sophisticated threat group linked to China has been actively exploiting critical vulnerabilities in Ivanti Endpoint Manager Mobile (EPMM) systems since May 15, 2025.
Their campaign targets organizations across multiple sectors, including healthcare, telecommunications, aviation, municipal government, finance, and defense, on a global scale.
The attackers are using two recently disclosed vulnerabilities, CVE-2025-4427 and CVE-2025-4428, which can be combined to allow unauthenticated remote code execution on vulnerable systems.
This widespread campaign has impacted victims in Europe, North America, and the Asia-Pacific region. Confirmed targets include local government entities in Scandinavian capitals, healthcare trusts in the United Kingdom, telecommunications firms in Germany, U.S.-based medical device companies, and automotive suppliers in Japan.
The group appears to be particularly focused on organizations that manage large numbers of mobile devices. By exploiting EPMM, which is central to enterprise mobile device management, the attackers aim to compromise potentially thousands of endpoints within affected networks.
According to analysts at EclecticIQ, this activity has been attributed with high confidence to UNC5221, a China-affiliated espionage group known for exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities in edge network appliances since at least 2023. The group has demonstrated in-depth knowledge of EPMM’s architecture, repurposing legitimate components to carry out covert data theft. The stolen data includes personally identifiable information, login credentials, and sensitive corporate records.
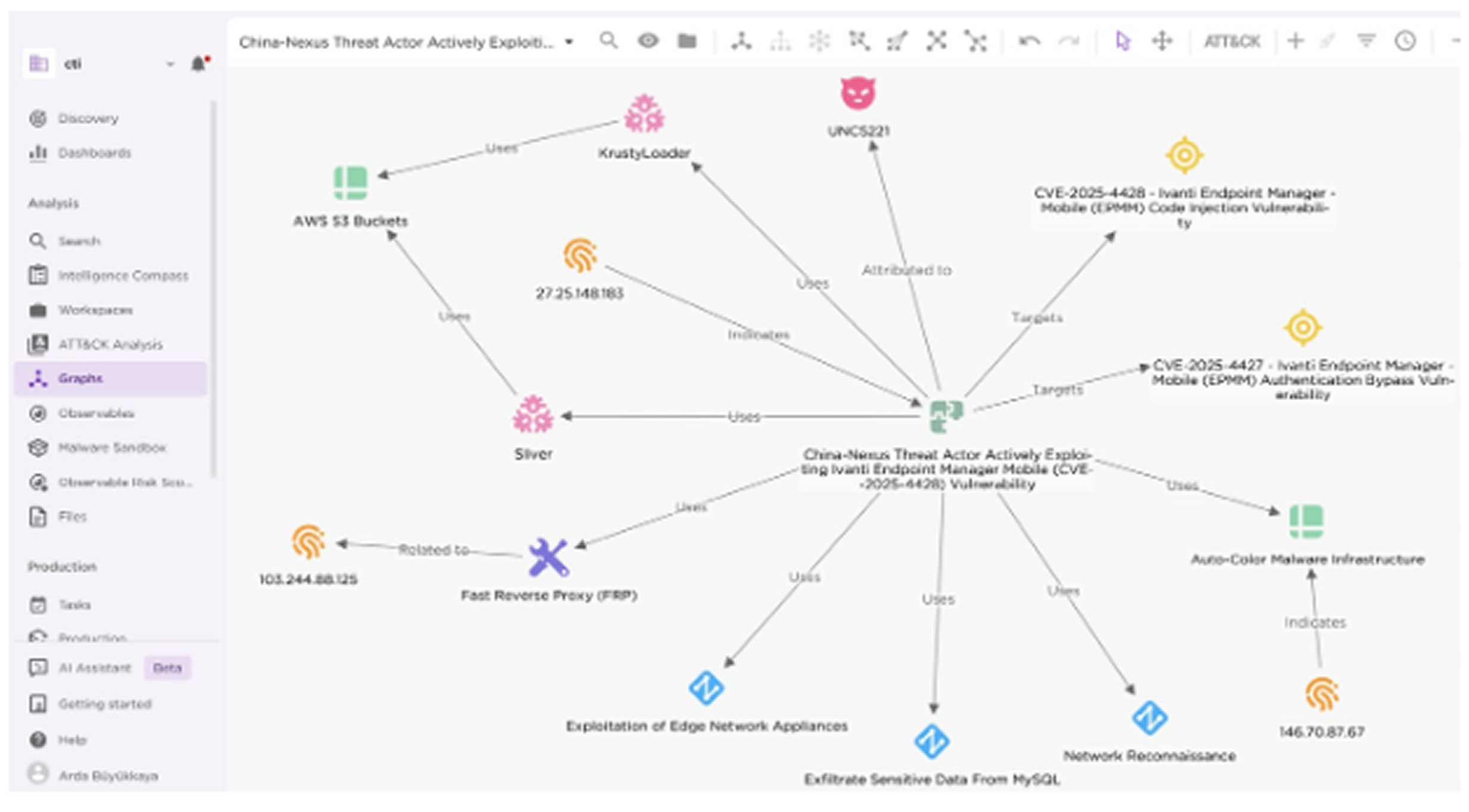
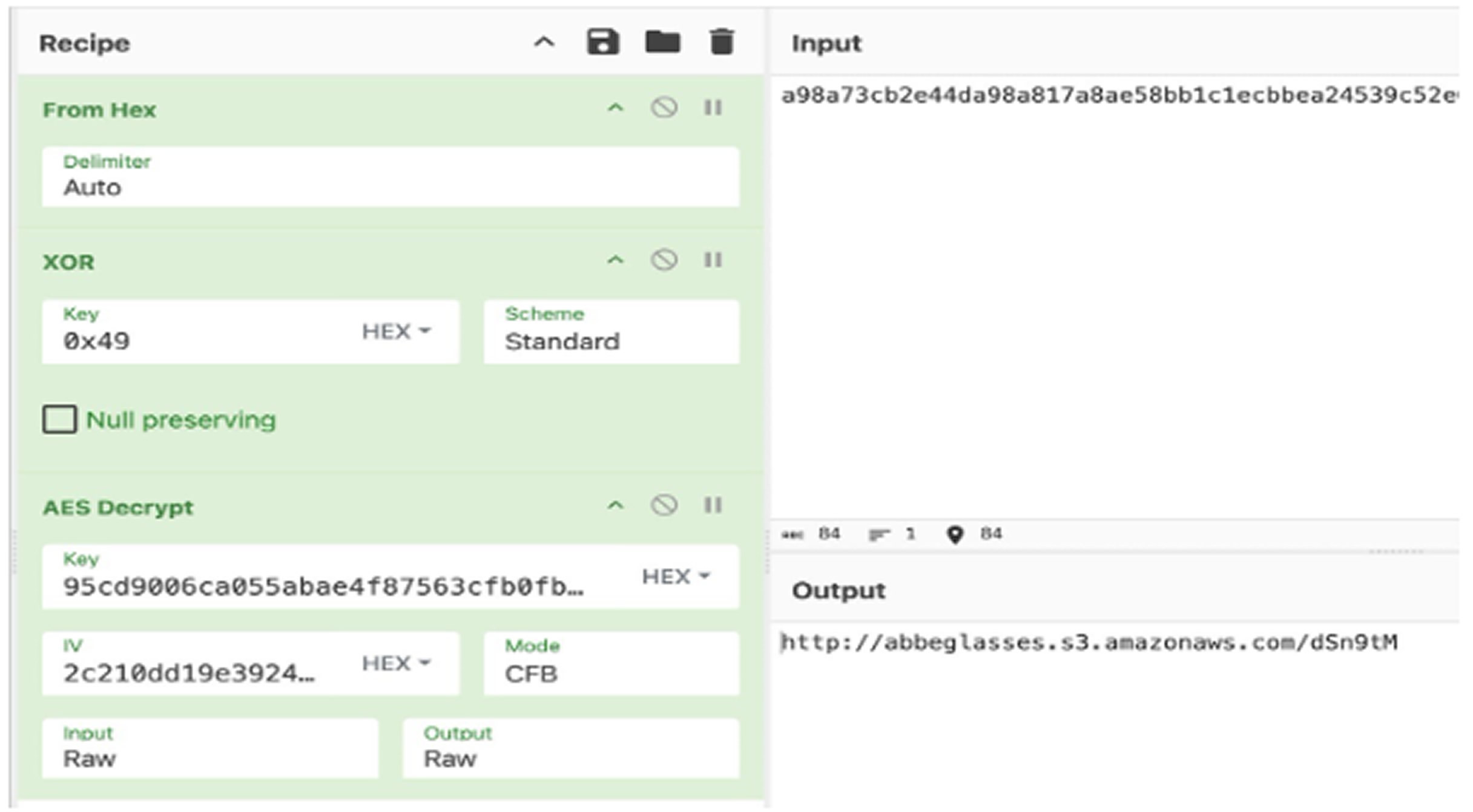
Among the tools deployed are KrustyLoader, which downloads encrypted Sliver backdoor payloads from compromised Amazon AWS S3 storage, and Fast Reverse Proxy (FRP), used to maintain long-term access for surveillance and lateral movement within networks. The level of technical skill and the chosen targets indicate that this campaign is part of a larger state-sponsored espionage effort, posing serious concerns about ongoing intelligence gathering and network breaches.
Initial Access and Exploitation Techniques
The threat actors begin by exploiting an unauthenticated remote code execution flaw at the /mifs/rs/api/v2/ endpoint, using the format= parameter to inject malicious commands.
They employ Java-based server-side injection methods, embedding intricate payloads in HTTP GET requests that exploit Java reflection to run arbitrary system commands. This method keeps the Java thread active until external processes finish, maintaining communication between the attackers and the compromised systems. This combination of techniques allows attackers to execute commands and retrieve results in real time, establishing effective command-and-control through Java-based vulnerabilities.
These advanced exploitation techniques highlight the threat group’s technical capability and its ability to rapidly turn newly discovered vulnerabilities into tools for extensive espionage.
Found this article interesting? Follow us on X(Twitter) ,Threads and FaceBook to read more exclusive content we post.



