Threat Actors Use Fake Websites and PowerShell Scripts to Deliver NetSupport RAT
Cybersecurity researchers are warning of a new malicious campaign that uses fake websites to trick users into executing harmful PowerShell scripts, ultimately infecting their systems with the NetSupport Remote Access Trojan (RAT).
According to the DomainTools Investigations (DTI) team, the attack involves multi-stage downloader scripts hosted on deceptive websites that mimic legitimate services such as Gitcode and DocuSign. These websites attempt to lure users into copying and running an initial PowerShell command through the Windows Run prompt.
Once executed, the script downloads another PowerShell-based downloader, which then retrieves and launches additional payloads. This chain of execution culminates in the installation of NetSupport RAT on the victim’s system. Researchers believe these fake sites are likely promoted through phishing emails or messages distributed on social media.
The malicious scripts found on the counterfeit Gitcode site initiate a sequence of downloads from an external server (tradingviewtool[.]com). These scripts are executed in order to deliver the final NetSupport payload.
In a similar variation of the attack, DomainTools also discovered phishing domains impersonating DocuSign, such as docusign.sa[.]com. These spoofed sites use a CAPTCHA-like verification process to trick users into launching the malicious PowerShell code. Victims are asked to prove they are human by completing the check, which silently copies an obfuscated PowerShell command to their clipboard. They are then instructed to open the Windows Run dialog, paste the code, and press Enter, unknowingly executing the script.
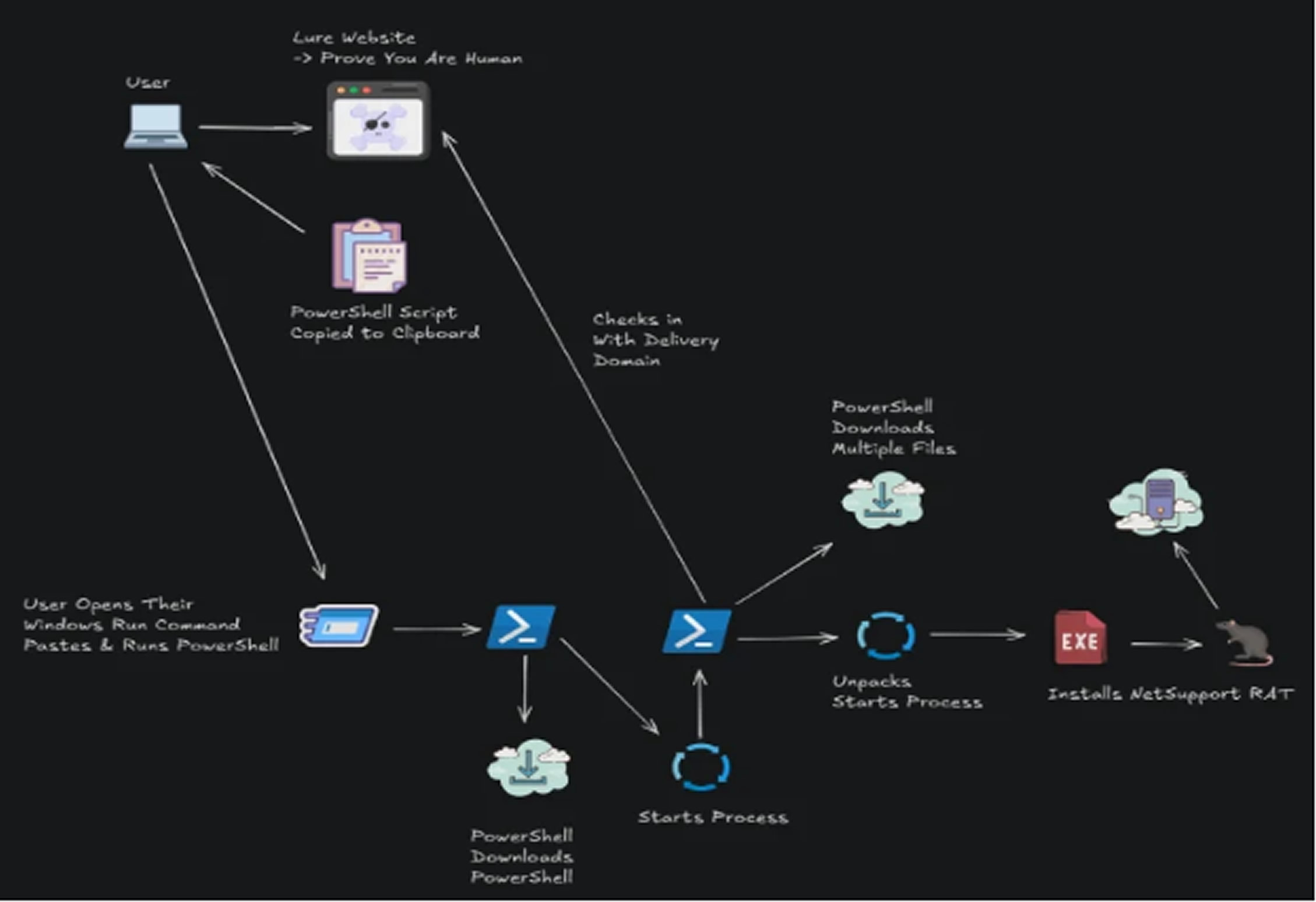
This script proceeds to download a file named "wbdims.exe" from GitHub, which is used to maintain persistence on the infected machine. Although the file was unavailable during the investigation, researchers suspect it communicates with the domain "docusign.sa[.]com/verification/c.php" to receive further instructions. Following this step, the browser refreshes and loads another script from "docusign.sa[.]com/verification/s.php?an=1."
That script delivers a second-stage PowerShell command, which downloads a ZIP archive from the same server. The archive contains an executable named "jp2launcher.exe," which is run to complete the infection process and deploy NetSupport RAT.
The use of multiple download and execution stages appears to be a strategy to avoid detection and increase the campaign’s resilience against security monitoring and takedown efforts.
Although the identities of the threat actors remain unknown, DomainTools observed overlaps in domain registration and delivery methods with a previous campaign associated with SocGholish (also known as FakeUpdates), which was discovered in October 2024.
It’s important to note that NetSupport Manager is a legitimate remote administration tool. However, cybercriminals frequently repurpose it for malicious use. Groups such as FIN7, Scarlet Goldfinch, and Storm-0408 have all used it as part of their remote access operations.
Found this article interesting? Follow us on X(Twitter) ,Threads and FaceBook to read more exclusive content we post.



