Golden Chickens Unveil Two New Malware Strains: TerraStealerV2 and TerraLogger
The cybercrime group known as Golden Chickens, also referred to as Venom Spider, has been linked to the emergence of two newly identified malware families TerraStealerV2 and TerraLogger. These developments signal the group's ongoing efforts to expand and refine its malicious toolkit.
According to researchers at Recorded Future’s Insikt Group, TerraStealerV2 is tailored to extract browser credentials, data from cryptocurrency wallets, and information from browser extensions. Meanwhile, TerraLogger functions as a standalone keylogger, using basic keyboard hooking techniques to record keystrokes and store them locally.
Golden Chickens, active since at least 2018, is known for its malware-as-a-service (MaaS) model, previously associated with the More_eggs malware. The group is believed to be operated by individuals based in Canada and Romania under the alias badbullzvenom. Other tools linked to this actor include lite_more_eggs, VenomLNK, TerraLoader, and TerraCrypt. In late 2023, Zscaler ThreatLabz uncovered new activity tied to the group, involving a backdoor named RevC2 and a loader called Venom Loader, both delivered via VenomLNK files.
The newly identified TerraStealerV2 has been distributed using multiple file formats such as EXE, DLL, MSI, and LNK and utilizes Microsoft’s OCX format (OLE Control Extension) for payload delivery, typically retrieved from a malicious domain (wetransfers[.]io). While it attempts to steal Chrome browser credentials by targeting the “Login Data” database, it fails to bypass Chrome’s Application Bound Encryption (ABE) introduced after July 2024, indicating the stealer is either outdated or still under development.
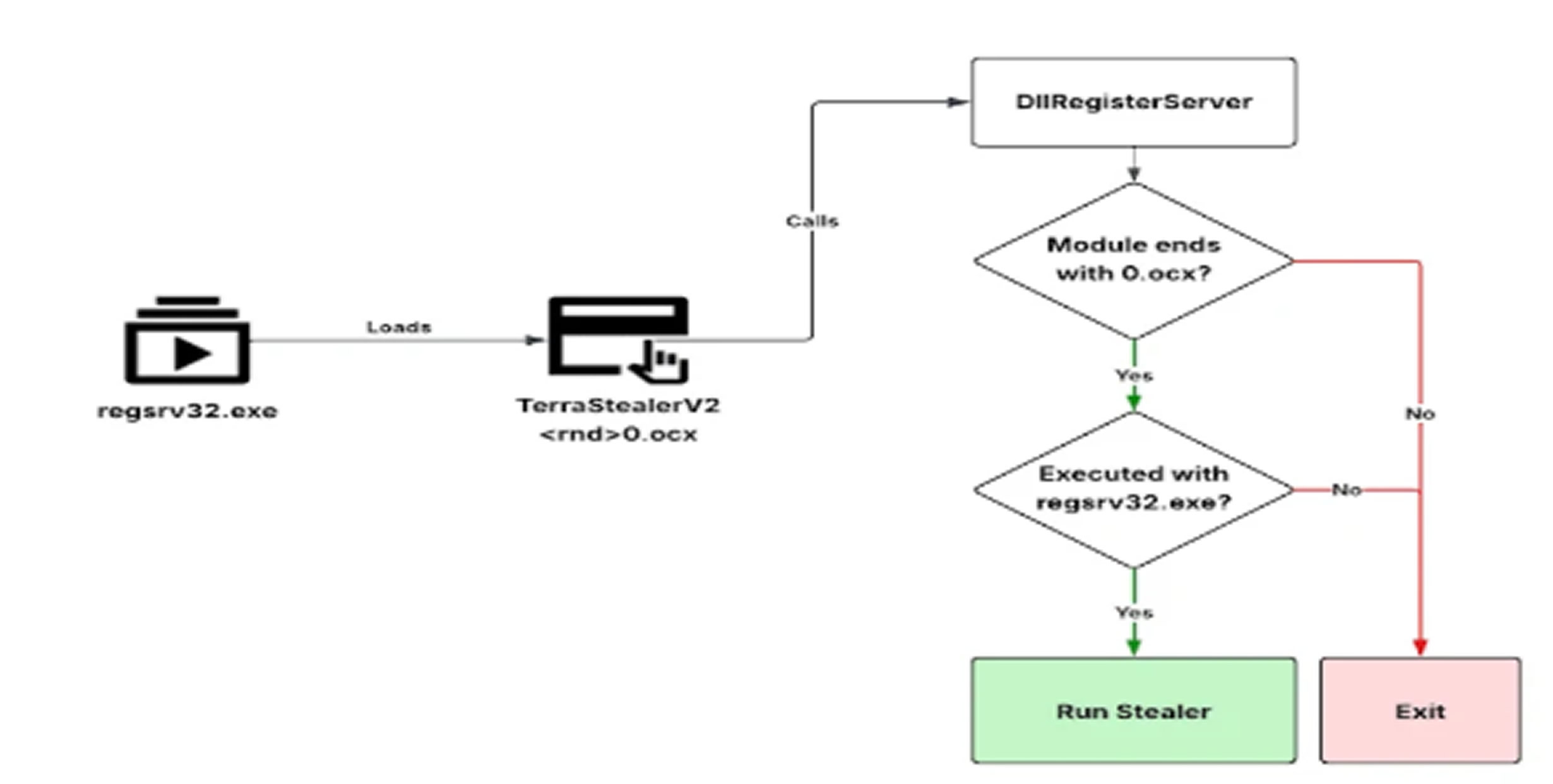
Data stolen by TerraStealerV2 is exfiltrated to both Telegram and the attacker-controlled domain. The malware also uses legitimate Windows utilities like regsvr32.exe and mshta.exe to evade detection and security tools.
On the other hand, TerraLogger, also delivered as an OCX file, solely logs keystrokes and lacks data exfiltration or command-and-control capabilities. This suggests it may still be in early development or designed to work alongside other malware components within the Golden Chickens' MaaS platform.
Recorded Future noted that both TerraStealerV2 and TerraLogger appear to be actively in development, lacking the stealth and sophistication seen in more mature Golden Chickens malware. However, given the group’s history of credential theft and access-based operations, these tools are likely to evolve further.
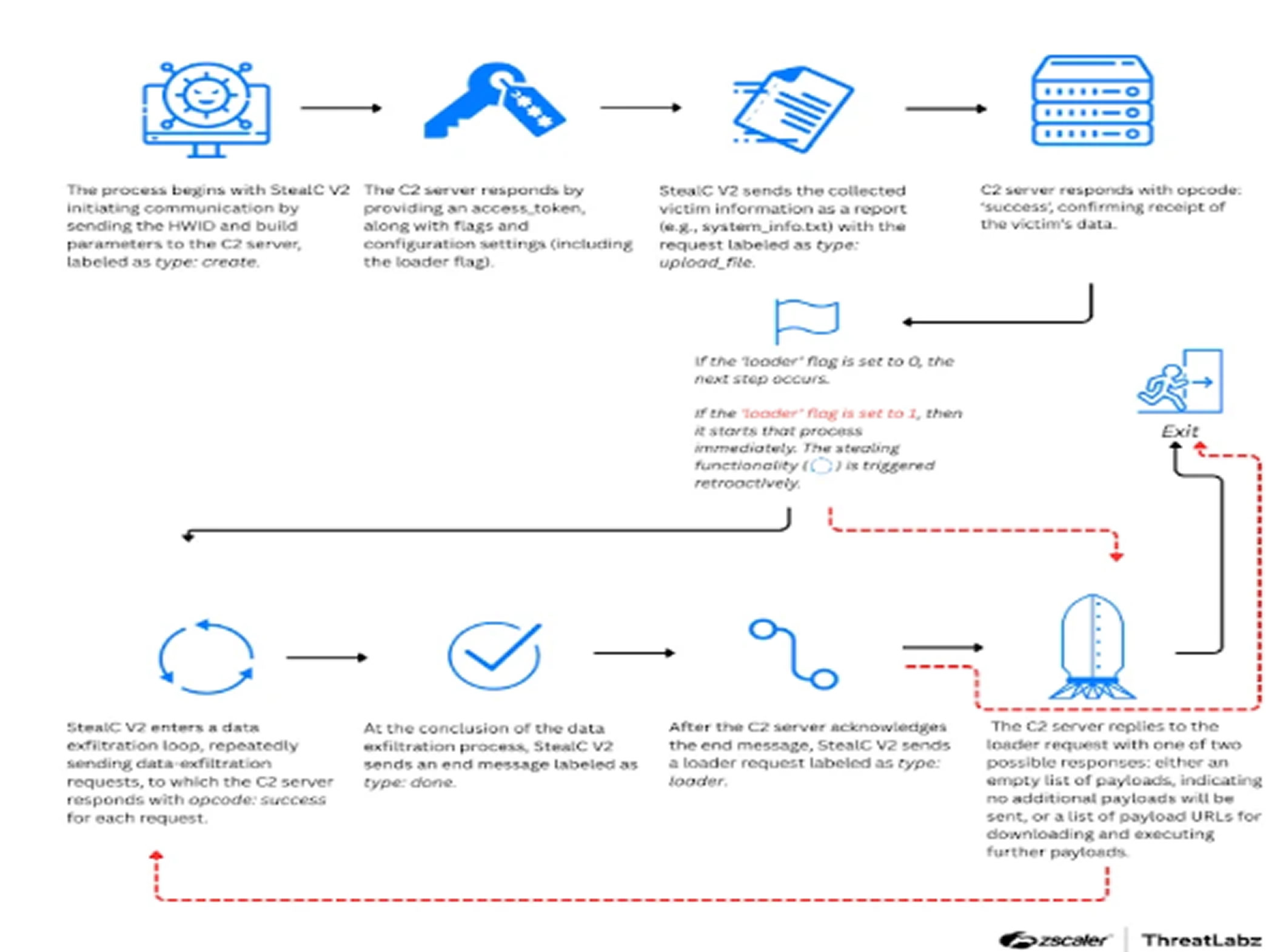
These revelations come at a time when several other stealer malware families have surfaced, including Hannibal Stealer, Gremlin Stealer, and Nullpoint Stealer, all engineered to extract a broad range of sensitive user data. Additionally, an updated version of StealC, dubbed StealC V2 (version 2.2.4) was detected in March 2025 with major upgrades.
According to Zscaler ThreatLabz, StealC V2 now supports MSI packages and PowerShell scripts for payload delivery. Its revamped control panel includes an integrated builder, allowing attackers to configure payload distribution based on geolocation, hardware ID, and installed software. The malware also offers capabilities like multi-monitor screenshot capture, advanced file grabbing, server-side credential brute-forcing, and Telegram bot integration for real-time notifications.
In summary, the continued enhancement of malware like TerraStealerV2, TerraLogger, and StealC V2 illustrates the persistent evolution of cybercriminal tools and the growing sophistication of threat actors like Golden Chickens.
StealC isn’t the only malware getting a makeover. Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered a revamped version of Lumma Stealer now rewritten in C++ that’s making rounds through the widely-used ClickFix social engineering tactic. This method lures users searching for cracked software, trending movies, or new music releases.
According to Google Security Operations, the updated variant, dubbed LUMMAC.V2, is a powerful information stealer targeting a broad array of applications. These include web browsers, cryptocurrency wallets, password managers, remote desktop tools, email clients, and messaging apps.
The malware extracts sensitive information such as login credentials, emails, system and user details, cookies, and screenshots. Once harvested, the stolen data is compressed into a ZIP file and sent to remote servers over HTTP, making it an efficient tool for cybercriminals.
Found this article interesting? Follow us on X(Twitter) ,Threads and FaceBook to read more exclusive content we post.


