A critical vulnerability identified as CVE-2024-0132 in NVIDIA’s Container Toolkit remains exploitable despite a previously issued patch.
The flaw continues to pose a significant threat to AI infrastructure and the protection of sensitive data due to the patch's incompleteness. In addition, a newly uncovered denial-of-service (DoS) vulnerability affecting Docker on Linux further complicates the situation. If exploited, these vulnerabilities could allow attackers to compromise systems, steal proprietary AI models, or disrupt essential services. Organizations that rely on NVIDIA’s Container Toolkit or Docker for AI and cloud-based workloads must act quickly to reduce exposure to these risks.
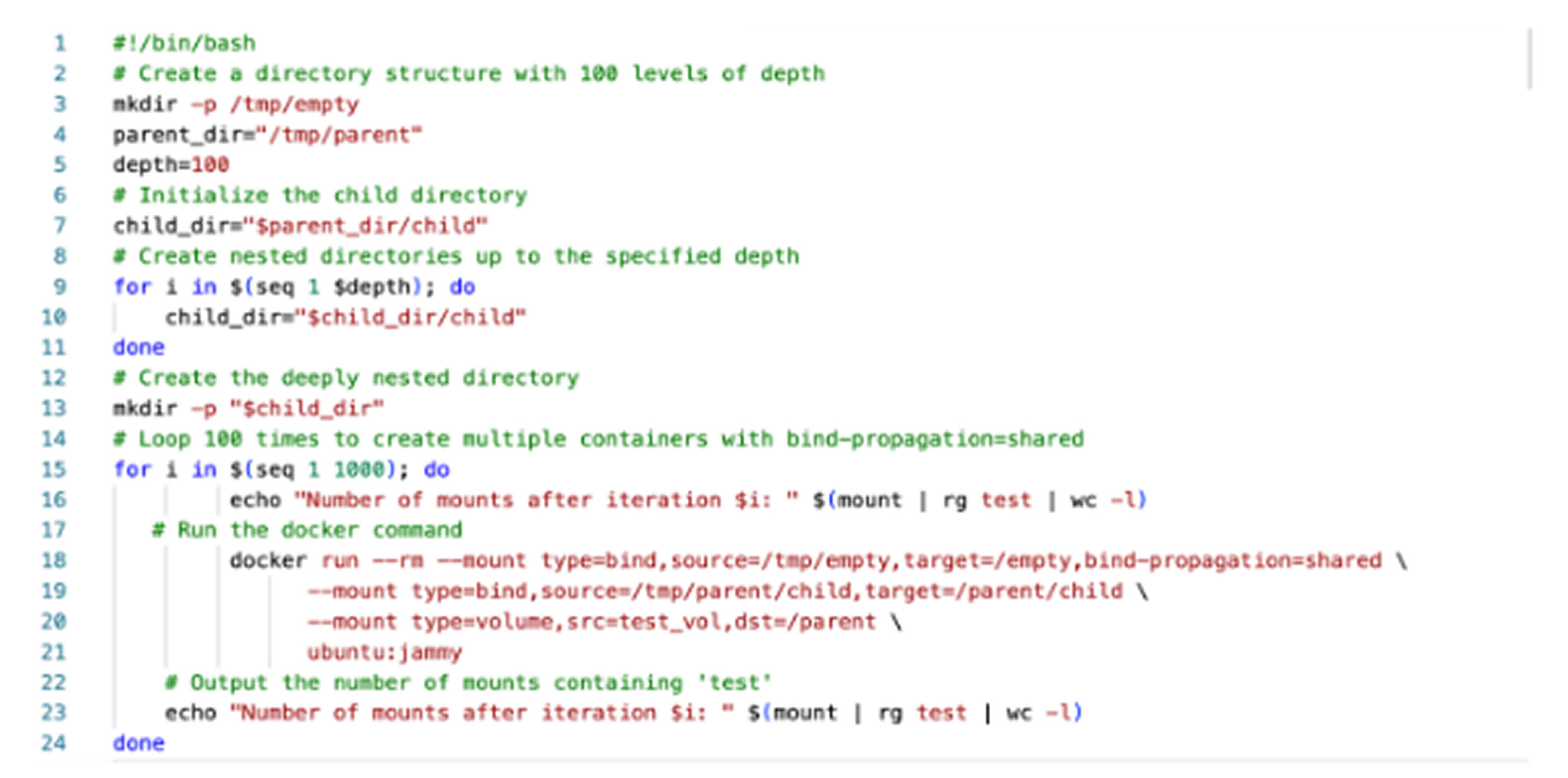
In September 2024, NVIDIA released a security update aimed at addressing CVE-2024-0132—a high-severity vulnerability rated 9.0 on the CVSS v3.1 scale. The flaw enables attackers to break out of container isolation and access the host file system, which could result in unauthorized access to sensitive information. A proof-of-concept demonstrated the severe impact, showing systems becoming unresponsive, halting container launches, and losing connectivity. The Docker security team emphasized that the underlying cause may involve issues with Docker's runtime or the Linux kernel’s mount behavior. They warned that access to the Docker API could equate to root-level control, raising serious security concerns. Both NVIDIA and the Moby project independently confirmed similar findings, urging prompt remediation.
The exploitation paths for these vulnerabilities are alarming. For CVE-2024-0132, an attacker could create malicious container images that exploit symlinked volumes, deploy them on targeted systems directly or through supply chain attacks, and trigger a race condition that allows access to the host file system. From there, attackers could utilize Container Runtime Unix sockets to execute arbitrary commands with elevated privileges, effectively taking full control of the system. Meanwhile, the Docker DoS flaw could enable attackers to exhaust system resources, bringing down AI workloads and other vital operations.
Organizations operating AI workloads, especially in sectors such as healthcare, finance, and autonomous technology are particularly at risk. Versions of the NVIDIA Container Toolkit up to 1.17.3 are vulnerable by default, while version 1.17.4 includes safer defaults but requires manual activation of key security features. Docker users, on the other hand, remain vulnerable to the DoS threat, which is especially dangerous in environments dependent on containerized applications like tech and logistics.
To mitigate these threats, Trend Research advises organizations to implement several security best practices. These include restricting Docker API access to authorized users only, disabling unnecessary features in Toolkit version 1.17.4, and scanning container images to block vulnerable instances before deployment. Monitoring mount tables for unusual growth, auditing container-to-host interactions, and deploying anomaly detection tools can help identify and respond to potential attacks. Additionally, organizations should rigorously test all patches to ensure they effectively address the vulnerabilities.
The persistence of CVE-2024-0132 and the emergence of the Docker DoS vulnerability underscore the ongoing challenges in securing AI and container-based systems. While updates from NVIDIA and Docker are anticipated, organizations must not wait. By proactively implementing layered security measures and continuously monitoring their environments, they can safeguard their operations and protect critical data assets from compromise.
Found this article interesting? Follow us on X(Twitter) and FaceBook to read more exclusive content we post.


