North Korean state-backed hackers, tracked as UNC5342, have adopted the sophisticated EtherHiding malware delivery technique, marking the first time a nation-state actor has been observed using this method. Since February, they have been employing this tactic in Contagious Interview social engineering campaigns designed to steal cryptocurrency.
EtherHiding and Campaign Tactics
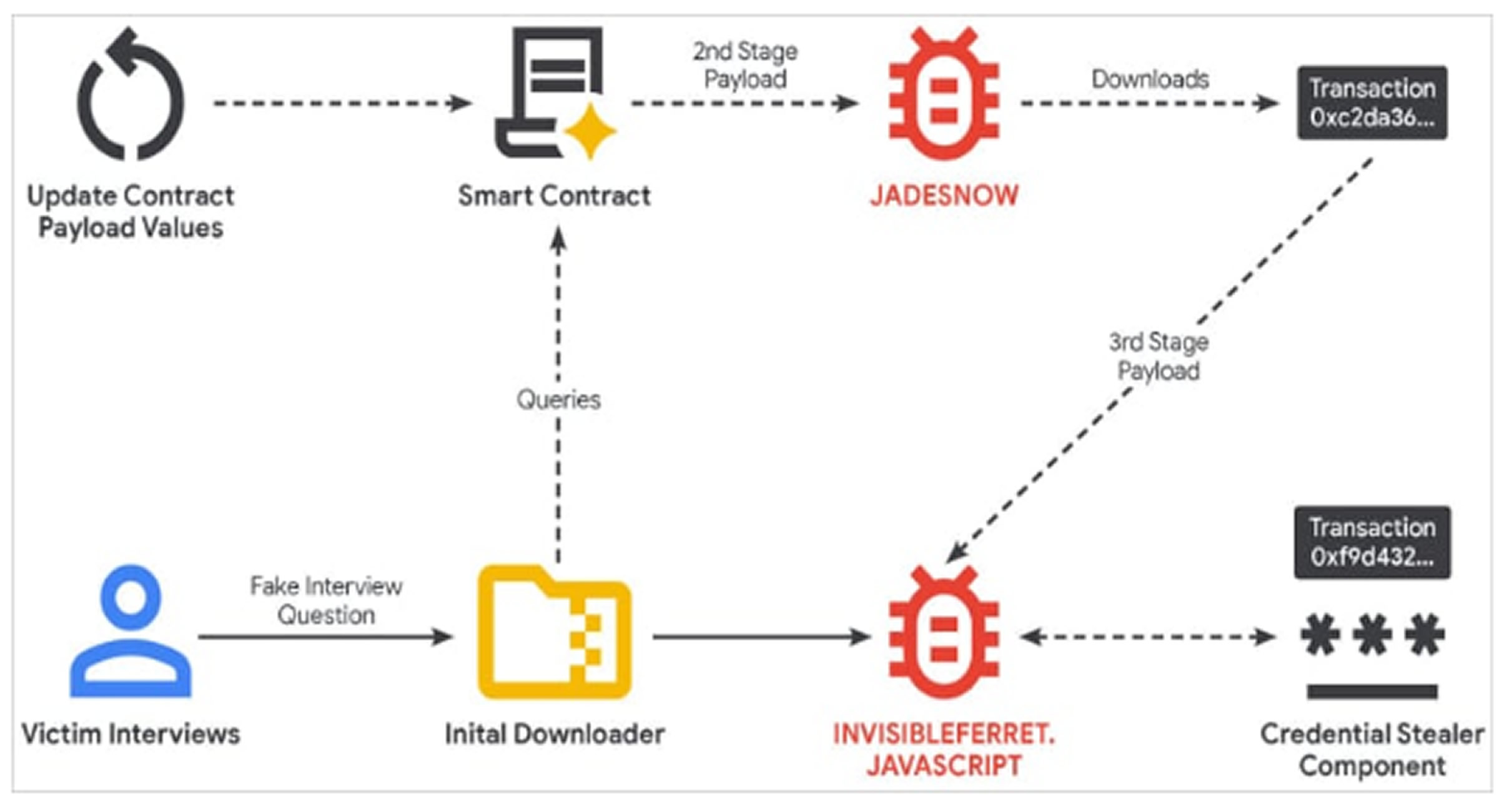
EtherHiding works by embedding malware payloads within smart contracts on a public blockchain, such as the Ethereum or Binance Smart Chain. This offers several key advantages to the attackers: it provides anonymity, makes the operation highly resistant to takedown attempts, and allows for flexible, low-cost payload updates. The payloads can be fetched using read-only blockchain calls, leaving no visible transaction history and adding stealth.
The attacks begin with fake job interviews, a signature social engineering method used by North Korean groups, targeting software and web developers. The attackers impersonate entities like BlockNovas LLC or SoftGlide LLC. Victims are tricked into running code as part of a technical assessment, which executes a JavaScript downloader known as JADESNOW.
Malware Payload and Stealer Component
The JADESNOW downloader interacts with the Ethereum or BNB Smart Chain to retrieve the next stage payload, which is a JavaScript version of the InvisibleFerret malware used for long-term espionage.
The credential stealer component deployed by the group specifically targets passwords, credit card information, and cryptocurrency wallet details (such as those from MetaMask and Phantom) stored in popular web browsers like Chrome and Edge.
The hackers are using multiple blockchains for their EtherHiding activity, which makes analysis more difficult and may indicate operational compartmentalization between different North Korean cyber units. The contract has been updated more than 20 times in the first four months, proving the attacker's ability to easily and frequently change the campaign's configuration at a low cost.
This adoption of blockchain-based malware delivery is a significant development that adds complexity to campaign tracking and disruption efforts. Individuals approached with suspicious job offers should remain cautious and test any requested downloads in isolated environments first.
Found this article interesting? Follow us on X(Twitter) ,Threads and FaceBook to read more exclusive content we post.



