Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered a previously undocumented and highly sophisticated threat actor named TA585. This group is running phishing campaigns to deploy an off-the-shelf malware called also known as Aurotun Stealer.
TA585's Complete Attack Chain
TA585 is unique because it manages its entire attack chain, including its own infrastructure, delivery, and malware installation. It does not rely on third-party brokers or traffic delivery systems. The group has used various sophisticated delivery techniques, including web injections and filtering checks.
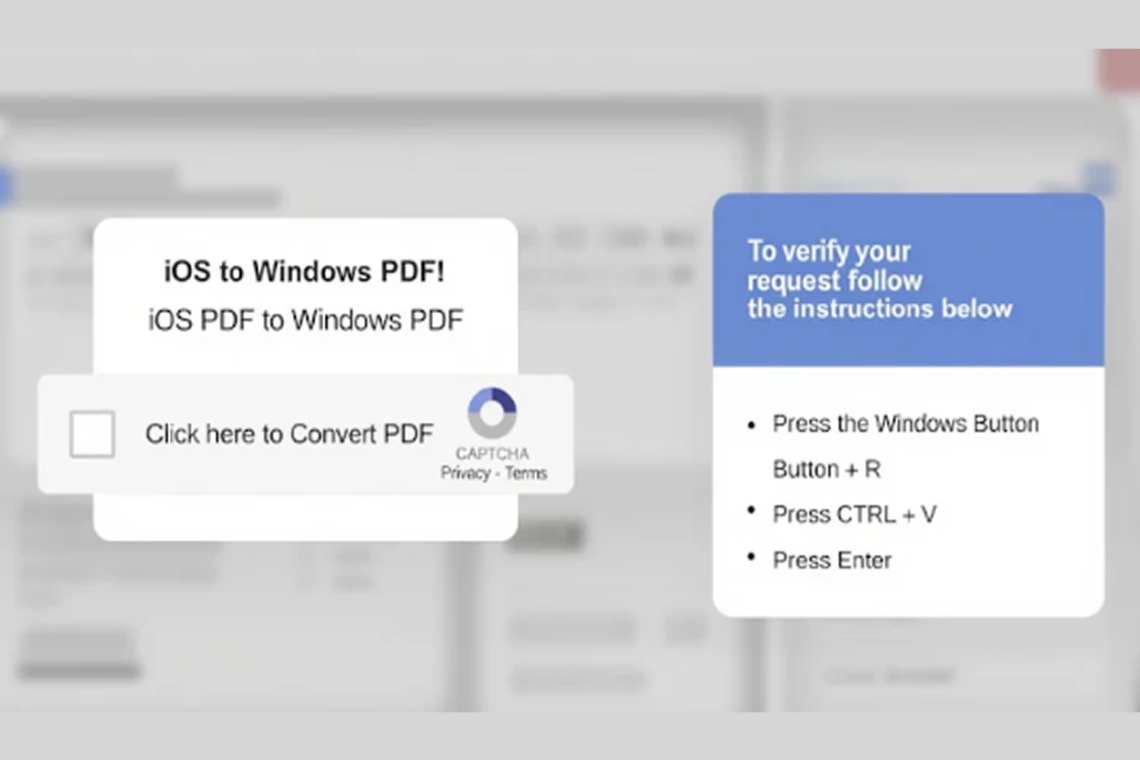
Early phishing campaigns used lures themed around the US Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to direct victims to malicious URLs. These pages employed a ClickFix social engineering tactic, tricking users into running a malicious command in the Windows Run dialog or PowerShell. This command executed a subsequent PowerShell script that delivered the MonsterV2 malware. Later attacks used malicious JavaScript injected into legitimate websites that served fake CAPTCHA verification overlays to initiate the attack.
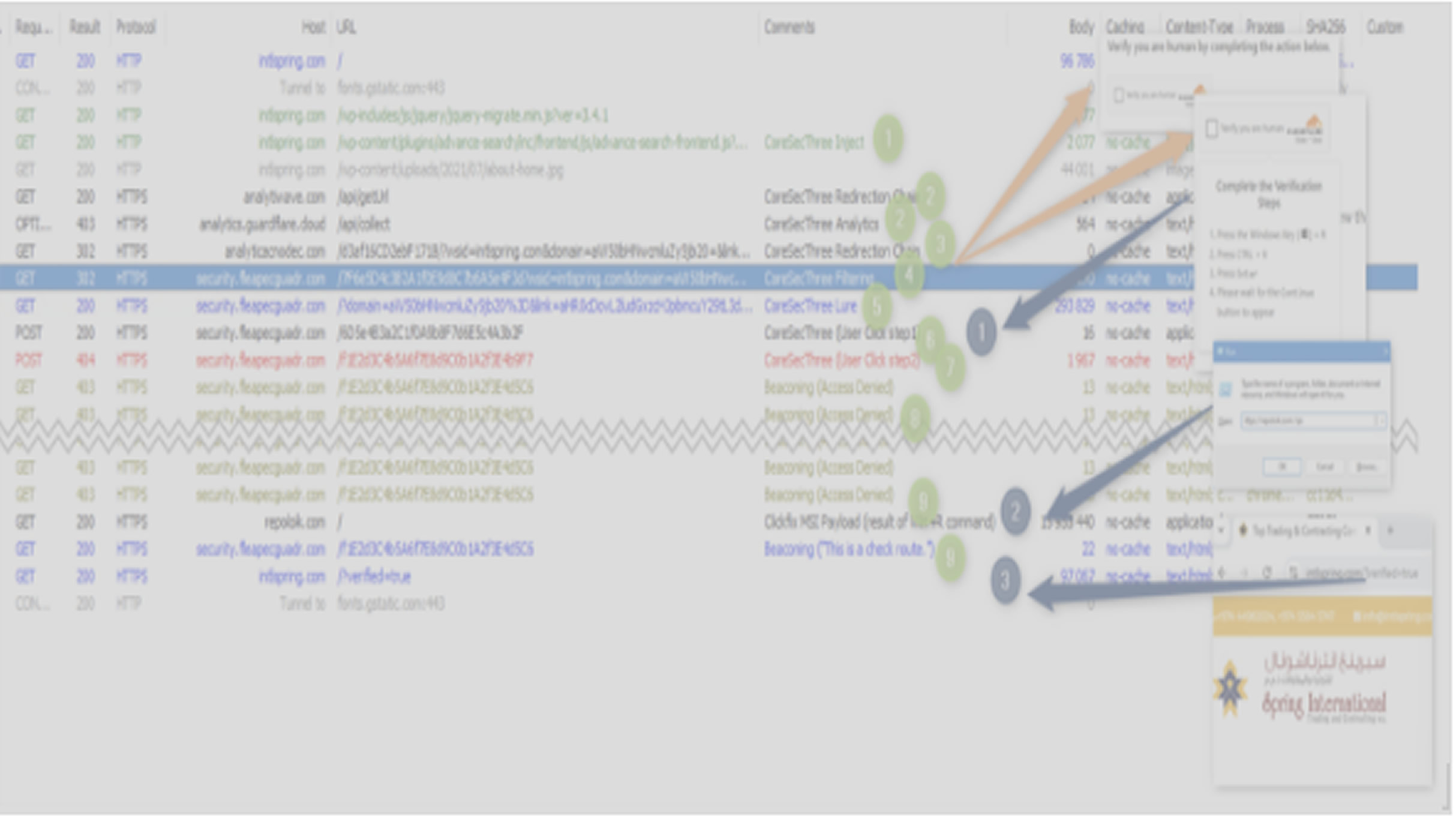
The actor has also been observed using email notifications from GitHub to tag users in bogus security notices, which contain links leading to actor-controlled websites. These web injects and GitHub alerts have been associated with CoreSecThree, a sophisticated framework used to propagate stealer malware since 2022.
MonsterV2 Malware Capabilities
MonsterV2 is a full-featured malware sold by a Russian-speaking actor for up to per month for the "Enterprise" version. It operates as a Remote Access Trojan (RAT), stealer, and loader, capable of:
- Stealing sensitive data and credentials.
- Acting as a clipper by replacing cryptocurrency addresses on the clipboard.
- Establishing remote control using Hidden Virtual Network Computing (HVNC).
- Executing arbitrary commands and downloading additional payloads like StealC and Remcos RAT.
To evade detection, MonsterV2 is packed using a C++ crypter called SonicCrypt and performs extensive anti-analysis checks. Notably, the malware avoids infecting computers located in Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) countries. If contact with the C2 server is established, the malware sends system information and geolocation, receiving commands to perform its malicious functions, including starting a keylogger, taking screenshots, and manipulating files.
Found this article interesting? Follow us on X(Twitter) ,Threads and FaceBook to read more exclusive content we post.