Google has introduced a new project called OSS Rebuild to improve the security of open-source package ecosystems and defend against software supply chain attacks.
According to Matthew Suozzo from Google’s Open Source Security Team, OSS Rebuild equips security teams with useful data to avoid compromise, without placing extra demands on package maintainers.
The initiative will start by supporting packages on Python Package Index, npm, and Crates.io, with plans to expand to other development platforms. It works by using declarative build definitions, build tracking tools, and network monitoring to generate security metadata. This metadata helps confirm that a package comes from a trusted source and has not been altered.
Google explains that OSS Rebuild uses automation and specific rules to create a build definition for each package, then rebuilds it. The rebuilt version is compared to the original, using a process that adjusts for technical variations like compression methods to make comparisons more accurate.
After the rebuild, the results and build definition are shared through SLSA Provenance, allowing users to confirm the package’s origin, reproduce the build, or modify it based on a trusted version.
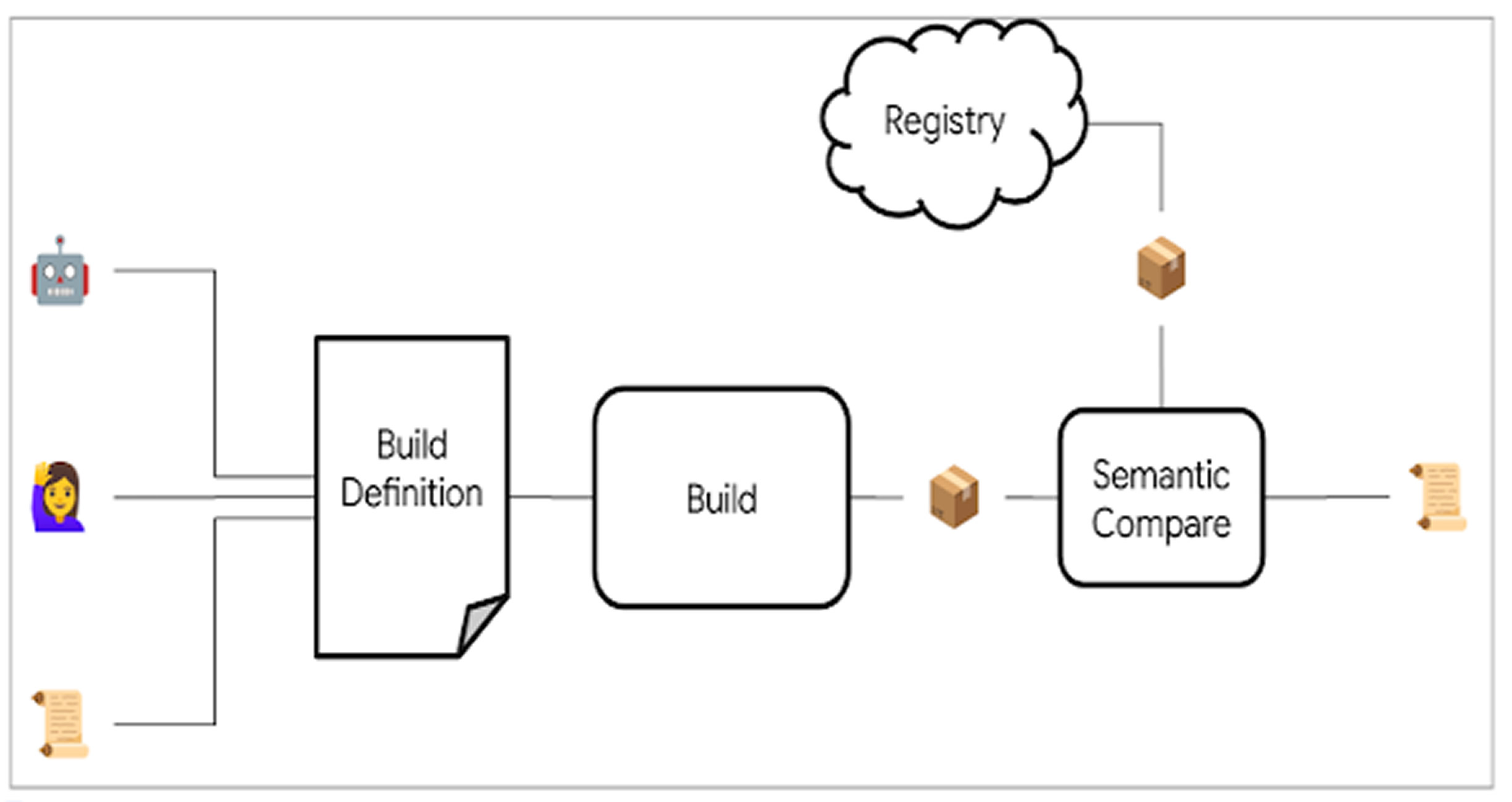
If a package cannot be automatically reproduced, OSS Rebuild provides a manual specification instead. Google says the system can uncover various supply chain threats, including:
- Code in published packages that does not appear in the source repository
- Unusual or suspicious build activity
- Hidden operations that are hard to detect manually, like those found in XZ Utils
Beyond protection, the tool helps generate better Software Bills of Materials, speeds up vulnerability management, increases trust in packages, and reduces the need for CI/CD systems to handle security tasks.
Google adds that rebuilds are based on public metadata and are tested against the original versions. When successful, the results are published as proof of integrity, helping eliminate many possible security risks.
Found this article interesting? Follow us on X(Twitter) ,Threads and FaceBook to read more exclusive content we post.



