FIN7’s New Python-Based Anubis Backdoor Evades Detection
Cybersecurity experts have uncovered a sophisticated backdoor tool developed by the notorious financial cybercrime group FIN7. Dubbed “Anubis Backdoor,” this Python-based malware marks a significant evolution in the group’s attack methods, leveraging advanced obfuscation and encryption to remain undetected.
The malware is delivered via phishing emails containing a seemingly harmless ZIP archive packed with multiple Python files. G Data researchers found that FIN7 uses legitimate programming techniques combined with obfuscation to hide malicious intent. Unlike previous campaigns, this Python-based approach allows the backdoor to blend seamlessly with normal system operations.
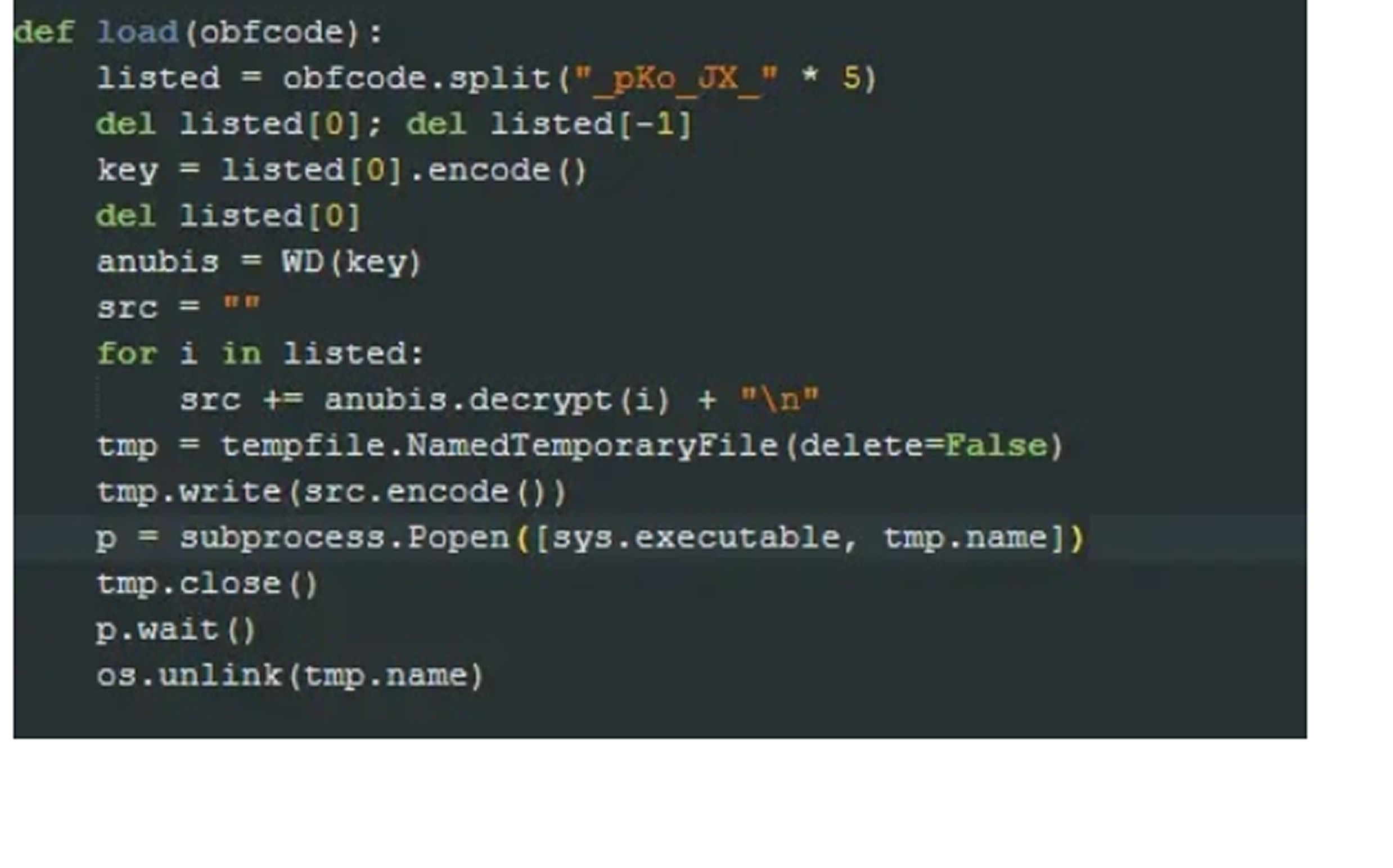
One of the most alarming aspects of Anubis Backdoor is its minimal footprint and anti-forensic capabilities. It employs temporary file execution and encryption to avoid detection, making analysis significantly more challenging. To maintain persistence, the malware stores its Command and Control (C2) configurations in the Windows Registry under randomized key names like HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\FormidableHandlers.
The malware communicates with its C2 servers over HTTP ports 80/443, using Base64 encoding and custom alphabet substitution to obfuscate its traffic. This level of stealth allows it to evade traditional network monitoring tools. Once inside a system, Anubis Backdoor grants full system control, enabling file manipulation, system reconnaissance, and real-time C2 updates.
At its core, Anubis Backdoor relies on a decryption mechanism that extracts encryption keys and executes decrypted code on the fly. Static analysis of the malware revealed default C2 servers at 38.134.148.20 and 5.252.177.249, along with a hardcoded agent identifier. Additionally, the key script, “conf.py,” exhibited exceptionally low detection rates on VirusTotal, demonstrating FIN7’s advanced obfuscation techniques.
Anubis Backdoor is a highly evasive and flexible attack tool that allows FIN7 to infiltrate and maintain access to corporate systems. Its ability to blend with normal network traffic makes it a serious cybersecurity threat for organizations worldwide.
Found this article interesting? Follow us on X(Twitter) and Instagram to read more exclusive content we post.


