A set of five critical security vulnerabilities have been identified in the Ingress NGINX
Controller for Kubernetes, potentially allowing unauthenticated remote code execution. These flaws expose more than 6,500 clusters to risk by making the component accessible via the public internet.
The vulnerabilities, tracked as CVE-2025-24513, CVE-2025-24514, CVE-2025-1097, CVE-2025-1098, and CVE-2025-1974, have been collectively named IngressNightmare by cloud security firm Wiz. Each has been assigned a CVSS severity score of 9.8. However, these issues do not impact the NGINX Ingress Controller, a different implementation for managing ingress in Kubernetes.
According to Wiz, exploiting these vulnerabilities grants attackers unauthorized access to all stored secrets across multiple Kubernetes namespaces, potentially leading to a full cluster takeover. The vulnerabilities primarily affect the admission controller component of the Ingress NGINX Controller. Research indicates that around 43% of cloud environments are susceptible to these exploits.
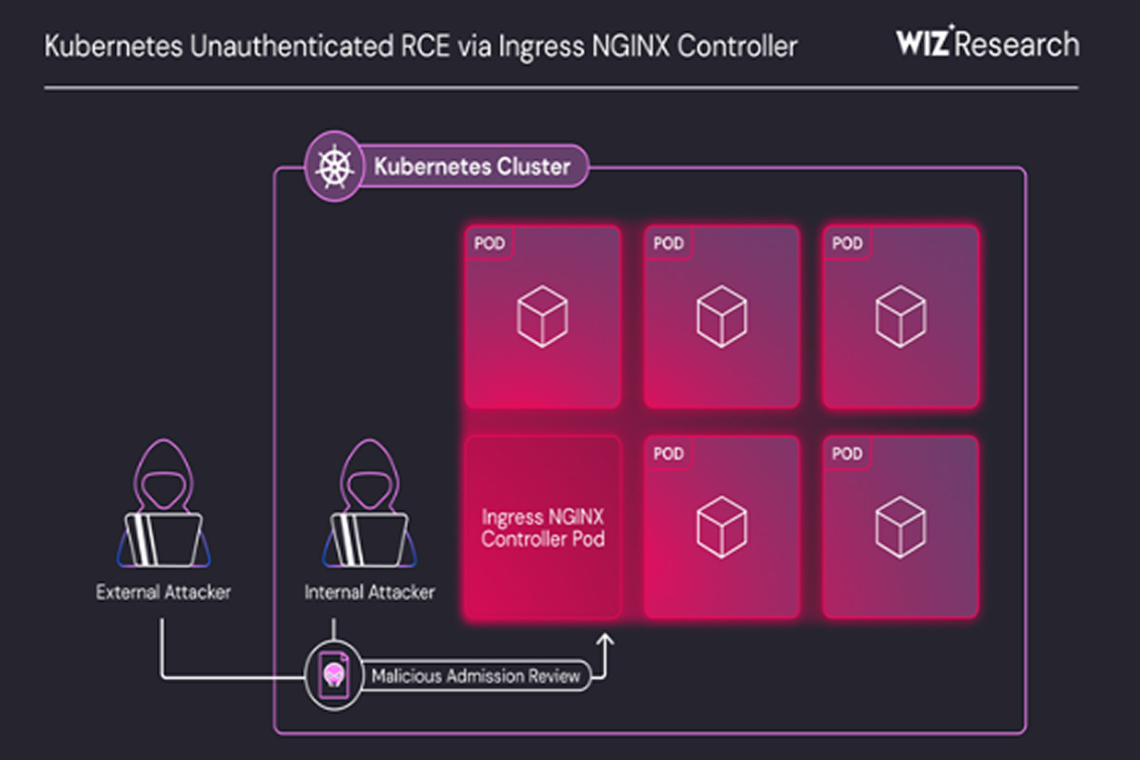
Ingress NGINX Controller functions as a reverse proxy and load balancer, facilitating HTTP and HTTPS traffic routing from external sources to services within a Kubernetes cluster. The attack capitalizes on the fact that admission controllers—which operate within Kubernetes pods—are network-accessible without authentication.
Hackers can exploit this flaw by injecting arbitrary NGINX configurations into the system. This is achieved by sending malicious ingress objects (AdmissionReview requests) directly to the admission controller, ultimately triggering remote code execution on the Ingress NGINX Controller’s pod.
“The elevated privileges and open network accessibility of the admission controller create a significant attack vector,” Wiz explained. “Exploiting this flaw allows an attacker to execute arbitrary code and access sensitive cluster secrets across namespaces, potentially leading to complete system compromise.”
The identified vulnerabilities include:
- CVE-2025-24514 – auth-url Annotation Injection
- CVE-2025-1097 – auth-tls-match-cn Annotation Injection
- CVE-2025-1098 – mirror UID Injection
- CVE-2025-1974 – NGINX Configuration Code Execution
In a test attack scenario, researchers demonstrated how a hacker could use NGINX’s client-body buffer feature to upload a malicious shared library into the pod. Then, by sending an AdmissionReview request containing a configuration injection directive, they could force the system to load the shared library, ultimately executing remote code.
Hillai Ben-Sasson, a cloud security researcher at Wiz, explained that the attack chain primarily relies on injecting malicious configurations to extract sensitive data and execute unauthorized commands. Attackers could leverage this method to escalate privileges and gain control over Kubernetes secrets, leading to full cluster compromise.
Following responsible disclosure, these vulnerabilities have been patched in Ingress NGINX Controller versions 1.12.1, 1.11.5, and 1.10.7.
To protect against exploitation, users should:
- Upgrade to the latest version of Ingress NGINX Controller immediately.
- Restrict access to the admission webhook endpoint, ensuring it is not exposed externally.
- Limit access to the admission controller, allowing only the Kubernetes API Server to communicate with it.
- Temporarily disable the admission controller component if it is not required.
These security measures are essential to prevent unauthorized access and protect Kubernetes environments from IngressNightmare attacks.
Found this article interesting? Follow us on X(Twitter) and Instagram to read more exclusive content we post.