A sophisticated new backdoor, dubbed Android.Backdoor.Baohuo.1.origin, has been discovered hidden within maliciously modified versions of the Telegram X messenger. The malware grants attackers complete, undetected control over victims' accounts.
Distribution and Scale of the Threat
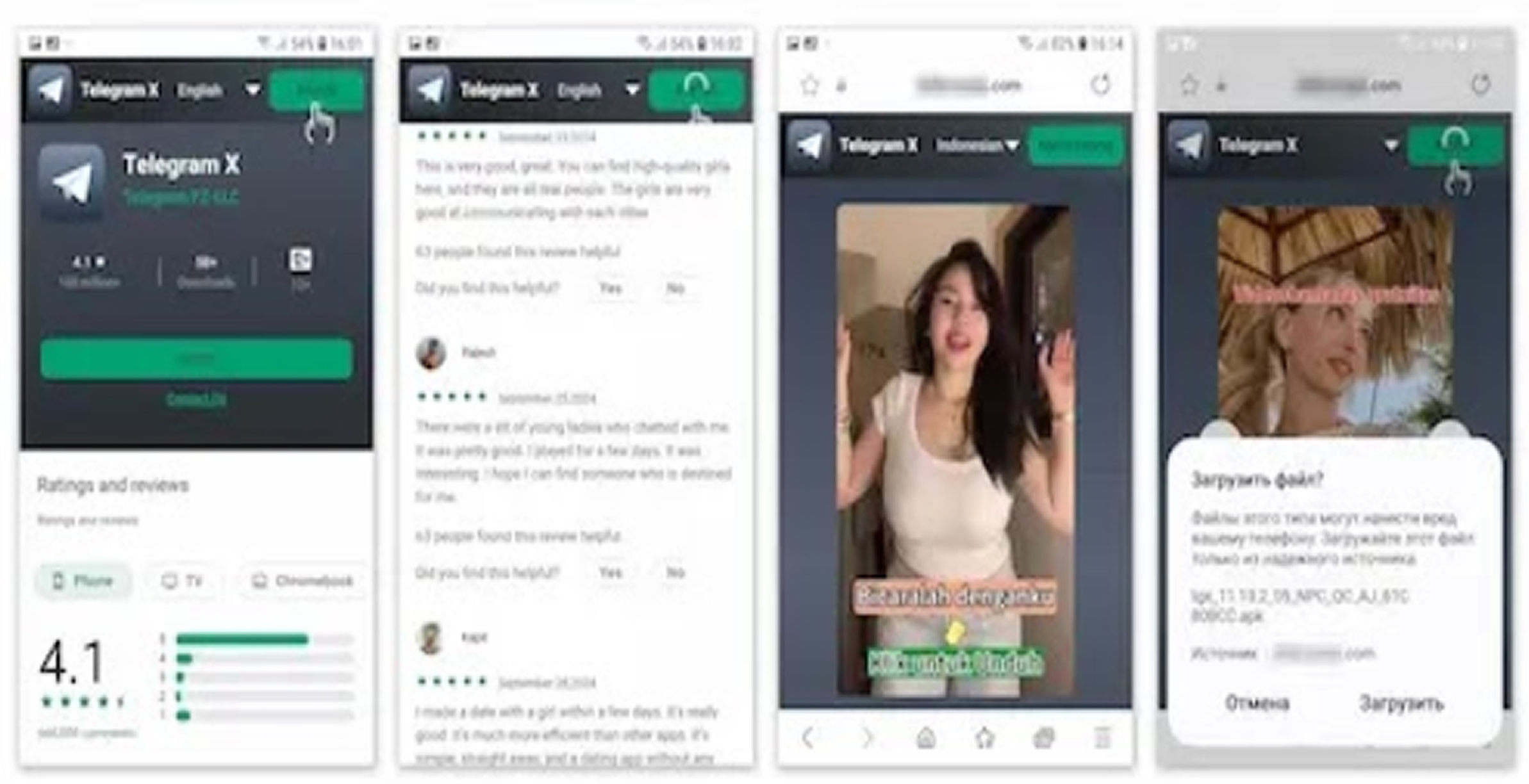
The malware infiltrates devices by masquerading as legitimate dating and communication platforms through deceptive in app advertisements and third-party app stores. Since mid 2024, the backdoor's distribution has primarily targeted Brazilian and Indonesian users, utilizing Portuguese and Indonesian language templates.
Victims are redirected from mobile app advertisements to fraudulent app catalogs featuring fake reviews. These sites deliver trojanized APK files that appear indistinguishable from legitimate Telegram X installations. With over 58,000 infected devices detected across approximately 3,000 models of smartphones, tablets, and even Android based vehicle systems, this represents a significant escalation in mobile malware sophistication. The threat has even infiltrated established third party app repositories such as APKPure, where it was deceptively posted under the official developer's name.
Unprecedented Redis C2
What truly sets Android.Backdoor.Baohuo.1.origin apart is its unprecedented use of a Redis database for command and control (C2) operations. While earlier versions relied on traditional C2 servers, the malware authors integrated Redis based command reception, marking the first documented instance of a Redis database being used in an Android malware control mechanism. Upon initialization, the backdoor connects to its traditional C2 server to retrieve the Redis connection credentials, allowing threat actors to issue commands and update settings remotely.
Account Hijacking and Espionage
Dr.Web analysts confirmed the malware’s exceptional capability to steal confidential information, including login credentials, passwords, and complete chat histories. The backdoor actively conceals its presence by hiding third party device connections from the active Telegram session lists.
Furthermore, it autonomously adds or removes users from channels and joins chats on the victim's behalf, transforming compromised accounts into tools for artificially inflating Telegram channel subscribers.
The malware employs the Xposed framework to dynamically modify core app methods, enabling advanced capabilities like hiding specific chats and intercepting clipboard contents. This clipboard monitoring allows for sophisticated data theft where victims inadvertently expose cryptocurrency wallet passwords, mnemonic phrases, or confidential business communications. The backdoor systematically collects device information, app data, message histories, and authentication tokens, transmitting this intelligence every three minutes while the app appears to function normally.
Found this article interesting? Follow us on X(Twitter) ,Threads and FaceBook to read more exclusive content we post.



